PTA103GIGU
PTA 103 Introduction to Clinical Practice 2
The following information is used for instructional purposes for students enrolled in the Physical Therapist Assistant Program at Lane Community College. It is not intended for commercial use or distribution or commercial purposes. It is not intended to serve as medical advice or treatment. Contact duyckm@lanecc.edu for permissions. Marc Duyck PTA, MEd. CSCS


A pharmacological approach to some gastrointestinal problems is appropriate in some cases
Active drains use suction to remove fluids
• Jackson-Pratt drains (JP) – closed drain (has a collector) that aids in removing fluid from abdominal wounds.
Drains to remove fluids post surgery
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/10/Post-operative_Jackson-Pratt_Drains.JPG
• Sump drains – open drain that also removes fluid by suction
Passive drains use pressure differentials and/or gravity to remove fluid
• Foley catheter - indwelling tube that collects urine
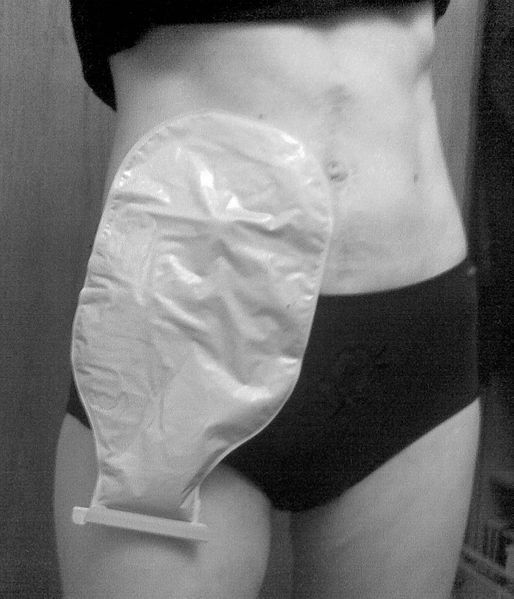
• Colostomy bag - external bag that collects fecal waste
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ileostomy_with_bag.jpg
![]()
Guided Learning #1. Guided learning to assist in table below and Goodman reading: just
over 10 min.
|
Anatomy |
Pathology |
Associated Terms |
Risk Factors |
Signs and Symptoms |
|
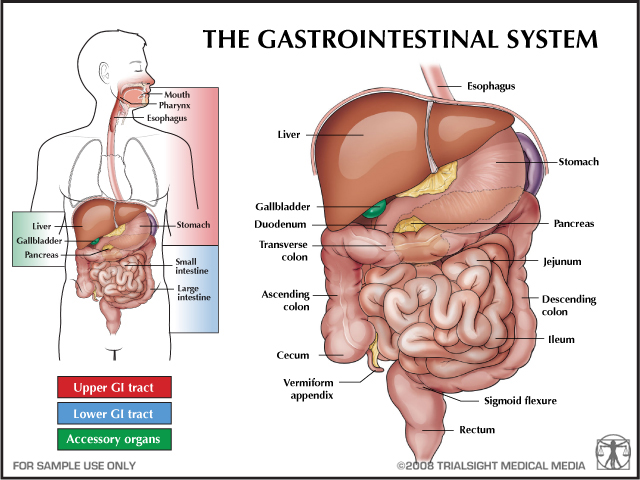
Upper GI |
Candidiasis Yeast Infection
|
Thrush |
Antibiotic use Immuno-suppression
|
Red, swollen mouth with white patches that can be scraped off Weigh loss due to pain in mouth with eating
|
|
Upper GI
|
Herpes Simplex 1 Viral Infection |
Cold Sore Fever blister
|
Contact by mouth with carrier/host
|
Burning blister in and around mouth. |
|
Upper GI |
Dysphasia |
Aspiration |
Neuromuscular impairment GI Disease
|
Difficulty with safe and effective, chew and swallow Coughing with eating and/or drinking
|
|
Upper GI |
Gastroesophageal reflex disease (GERD) Reflux of gastric contents into stomach
|
Acid Reflux Barium Swallow Endoscopy
|
NSAID use alcohol use. Infection. Smoking/tobacco use. Excessive acid production
|
Heartburn Regurgitation Esophagitis Dysphagia Pain (sub-sternal, non-cardiac) Sore or hoarse throat Hematemesis
|
|
Upper GI |
Barrette's Esophagus Change in epithelial cell morphology
|
Chronic GERD |
Alcohol use and smoking, chewing tobacco use may lead to esophageal cancer
|
Same as GERD with increased severity
|
|
Upper GI |
Esophageal Cancer
|
Squamous carcinoma Achalasia Stricture
|
EtOH/alcohol abuse. Smoking. Diet imbalances
|
Same as GERD, with increased severity, weight loss, pain
|
|
Stomach |
Gastritis Inflammation of inner stomach layer (mucosa) Can lead to electrolyte imbalance
|
Dyspepsia |
Trauma Salmonella infection NSAID Aspirin Alcohol related renal failure Liver failure Mechanical ventilation >48 hrs
|
Hemorrhage Fever Epigastric Pain Nausea Anorexia Hematemesis
|
|
Stomach |
Peptic Ulcer Disruption of the gastric or duodenal mucosa
|
Bleeding Perforation Obstruction
|
Excessive alcohol use Diet Stress NSAIDs Bacterial infection
|
Burning, gnawing pain Reduction of pain with eating Burping Nausea and/or vomiting Bleeding
|
|
Lower GI
|
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Colon Dysfunction |
BRAT diet (banana, rice, apple, tea or toast)
|
Stress Decreased sleep Dietary exacerbations (wheat, rye, barley, milk, EtOH, caffeine)
|
Alternating loose stools and constipation Bloating with abdominal pain Cramping Mucous/blood in stool
|
|
Lower GI |
Crohn's Disease Inflammation of intestinal wall
|
Ileitis Enteritis
|
Unknown Possible autoimmune response to bacterial or viral infection
|
Abdominal pain Diarrhea Occasional. Rectal bleeding Weight loss Small bowel obstruction Fistula formation Nutritional Deficiencies
|
|
Lower GI |
Ulcerative Colitis Inflammation of colon and /or rectum
|
Inflammatory bowel disease
|
Unknown Possible autoimmune response to bacterial or viral infection
|
Alternating loose stools and constipation Bloating with abdominal pain Cramping Mucous/blood in stool
|
|
Intestinal |
Whipples Disease
Bacterial mal absorption condition
|
Malnourishment
|
Exposure to Tropheryma Whippelli
|
Abdominal pain Weight loss Incomplete breakdown of intestinal materials Diarrhea Intestinal bleeding Fatigue and Weakness
|
|
Intestinal |
Short Bowel Syndrome Disorder from surgery where >50% of small intestine is removed Mal absorption condition
|
Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) |
History(Hx) of abdominal surgery Crohn's IBS Intestinal Trauma
|
Weakness Fatigue Depression Dehydration Weight loss Diarrhea Cramping and bloating Heart burn Weight Loss Diarrhea Malnourishment
|
|
Intestinal |
Diverticulosis Small outpourings or hernia in intestinal wall
|
Diverticulitis Intestinal necrosis
|
Advanced age Low fiber diet |
Abdominal pain Fever and chills Nausea and vomiting Cramping Constipation Fistula formation
|
|
Intestinal Bowel & Abdomen |
Ostomy Surgical opening from bowel or intestine to the outside. |
Ileostomy (removal of colon and rectum) Colostomy (removal of colon)
|
History of cancer, intestinal disease Trauma
|
External pouch for collection and elimination of waste
|
|
Intestinal and Abdominal |
Hernia Abdominal protrusion through a weak area in the abdominal wall
|
Inguinal (groin) Abdominal Femoral Hiatal Hernia or hernioplasty (reduction hernia and abdominal reinforcement)
|
Obesity heavy lifting straining during bowel movements Pregnancy Impaired nutrition Placement of abdominal drains General debility
|
Groin pain Palpable lump in groin Bowel obstruction Relief with applying pressure to bowel area/rectum or lower abdominal area. Shortness of breath
|
|
Vascular |
Hemorrhoids |
Sitz Baths |
Age (>50 yrs) Straining during bowel movements Chronic constipation
|
Pain Discomfort in sitting Itching Bleeding (anal canal and/or rectum)
|
|
Liver |
Jaundice Excessive bile production
|
|
Cirrhosis Hemolytic anemia
|
Yellowing of skin, eyes and fingernails
|
|
Liver |
Cirrhosis Fibrosis of liver tissue
|
Fatty liver. Alcoholic |
Hepatitis B, C, D Drugs and infection Autoimmune hepatitis
|
Effects multiple body systems |
|
Liver |
Hepatitis Inflammatory process in the liver; typically viral
|
Blood born pathogen
|
Viral infection EtOH/alcohol abuse
|
Effects multiple body systems
|
|
Gall Bladder |
Cholelithiasis
|
Gallstones |
Gender (Female), hx of diabetes, obesity. Ethnicity/higher in Native American and Hispanic communities versus African American/Caucasian.
|
Severe epigastric or right upper quadrant pain Referred pain under the right scapula Indigestion after eating fatty foods Nausea and/or vomiting
|
|
Pancreas |
Pancreatitis Inflammation of pancreas
|
|
EtOH/alcohol abuse, calcium malabsorption. Infection Abdominal trauma
|
Abdominal Epigastric pain (worse with walking, supine, eating) Abdominal swelling Nausea or vomiting Fever Dehydration Hypotension Pain radiating to low back |
Guided Learning #2 Liver Associated Health Conditions Guide to Goodman Readings
Just over 13 min
Guided Learning #3 Pancreas and Gall Bladder Associated Health Conditions Guide to Goodman Readings
Just over 7 min
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Classified by Body Mass Index of >+30kg/m2
Do you know your Body Mass Index? Calculate it here
(Lustig, Brindis, & Schmidt, 2012)
People with obesity are more likely to have malignancies in the GI tract as associated with the cause of death (Saab & Salvatore, 2015)

Image represents the relationship between mental health
and the health condition related to the gastrointestinal system
• decline in function due to restricted activity
• musculoskeletal pain (bone and joint)
• negative health perception
• anxiety and depression - including in children and adolescents
• increased personal health care costs
• increased incidence of disability
• increased discrimination and abuse
• increased risk for negative or biased health care decisions from health care providers (Casazza, et al., 2013).
• decreased access to treatment spaces and medical equipment during encounters with providers (e.g., BP cuffs, gowns, exam tables, scales)
• 5-10% reduction can produce measurable health benefits
• Decreased absenteeism from work reported from surgical and non-surgical weight loss programs
• Patients who are morbidly obese (BMI > 40 kg/m2, or 100 pounds over ideal weight) may qualify for bariatric surgery (gastric bypass) for weight control
![]()
![]()

The physical therapist prioritizes interventions within the physical therapy plan of care by integrating knowledge of body structure and function, participation restrictions, and contextual factors that inform prognosis and physical therapy diagnosis. Patient education in lifestyle factors that influence GI system disease should be integrated into a plan of care, with collaborative coordination with the medical and behavioral healthcare team as indicated. Patients with GI dysfunction may often present with co-morbidities in the integument, cardiopulmonary, and musculoskeletal systems. Physical therapy providers should self-assess and seek opportunities for professional development specific to metabolic and GI dysfunction in order to minimize bias and reduce negative perceptions of patients in this population.

A strong PT/PTA or inter professional team will result in a more positive outcome
for the patient
• Maintain positive, open, timely, patient-centered communication
• Delegate and accept responsibilities for treatment based on the skill level of the PTA
• POC
– PT: Modify and update POC based on progress reported or reassessment
– PTA: Document patient status (progress/barriers) and request clarification or input as needed depending patient response and skill set
A ROM assessment is part of the musculoskeletal system overview
hen treating a pt. with a gastrointestinal health condition
Aerobic Capacity and Endurance
Anthropometrical Characteristics
Arousal, attention, cognition
Pain
Joint Integrity and Mobility
Neuromuscular tests
Functional Activity Performance

Transfer training may be part of the plan of care for a pt with a gastrointestinal health condition
1. Log rolling/bracing with pillow
2. Transfer training
3. Endurance training (gait, exercise)
4. Postural training
Incentive spirometers may be used
especially in the acute setting for respiratory health for a pt with
a gastrointestinal health condition
1. breathing exercises
2. incentive spirometry
3. huffing/directed cough
4. chest percussion and vibration
1. Wound care for incisions
2. Skin/wound care for ostomies
3. Generalized skin care and education skin inspection for at-risk areas
1. Training in adaptive devices and equipment
2. Environmental assessment and modifications

Shoulder ROM and breathing exercises can help
prevent other health conditions
Education in
1. Lifestyle modification/decreasing risk of recurrence
2. Energy conservation (pacing and prioritizing)
3. Ostomy care
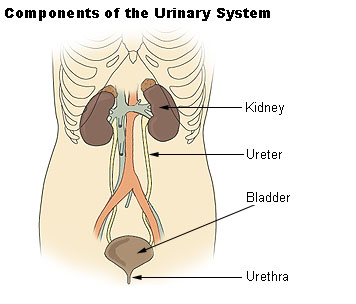
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Illu_urinary_system.jpg
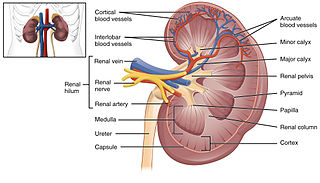
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/87/2610_The_Kidney.jpg/320px-2610_The_Kidney.jpg
Fluids are filtered through the kidneys and the filtrate is converted to urine. Urine is mostly water and urea, which is a metabolic by-product of protein metabolism, and electrolytes
Urination is mediated by voluntary and involuntary nervous system actions:
![]()
![]()
![]()

Medical News Today|1100 × 734 jpeg

https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Blausen_0595_KidneyStones.png
![]()

Blunt trauma to the kidneys can occur in a bike accident


Incontinence pads - these products are progressively improving to help support dignity and function
![]()

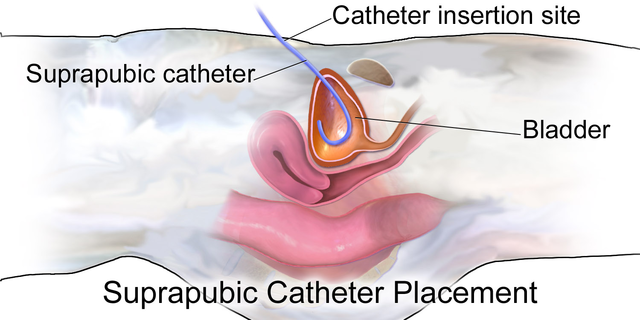
A pt who has a spinal cord injury health condition can be at a higher risk of having a Neurogenic bladder condition
.png)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Benign_Prostatic_Hyperplasia_(BPH).png
This link provides a refresher of the GU A&P and then goes into BPH and TURP descriptions
This device is used by men to collect urine when unable to use a commode or toilet

Incorrect billing can have a significant impact on a patients pocketbook or bank
• Document minutes spent providing direct patient care (can include set up and patient communication/family training if patient is present)
• Consider the impairment you are treating when selecting an appropriate billing code
– Endurance (therex – 97110 or ther act – 97530)
– Joint mobility (therex – 97110)
– Functional mobility (ther act -97530)
– Breathing exercises ( therex – 97110)
– Energy conservation techniques ( ther act – 97530)
– Chest PT (manual therapy – 97140)
-- Gait Training (97116)
American Urological Association. 2021. What is Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy? Available at: https://www.urologyhealth.org/urologic-conditions/benign-prostatic-hyperplasia-(bph)
Elsevier. 2019. Innervation of Urinary Bladder and Lower Ureter. Available at: file:///C:/Users/Marc/PTAEthics/PTA103wk8GIDisorders/index.html
Health Grades. (2015). Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy. Retrieved from http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/animations/benign-prostatic-hyperplasia-bph.htm
Casazza, K., Fontaine, K. R., Astrup, A., Birch, L. L., Brown, A. W., Bohan Brown, M. M., ... & McIver, K. (2013). Myths, presumptions, and facts about obesity. New England Journal of Medicine, 368(5), 446-454.
International Foundation for Functional Intestinal Disorders. (2021). Lower GI disorders. Retrieved from https://www.iffgd.org/lower-gi-disorders.html
International Foundation for Functional Intestinal Disorders. (2021). Upper GI disorders. Retrieved from https://www.iffgd.org/upper-gi-disorders.html
Kaur, J., Lamb, M. M., & Ogden, C. L. (2015). The association between food insecurity and obesity in children—The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 115(5), 751-758.
Lustig, R. H., Schmidt, L. A., & Brindis, C. D. (2012). Public health: The toxic truth about sugar. Nature, 482(7383), 27-29.
Mayo Clinic. (2021). Cystitis. Retrieved from http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cystitis/basics/definition/con-20024076
Mayo Clinic. (2021). Pancreatitis. Retrieved from http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pancreatitis/home/ovc-20252596
McGraw Hill. (2020). Animation Micturition Reflex. Retrieved from http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter27/animation__micturition_reflex.html
Pizzi, M. A., & Vroman, K. (2013). Childhood obesity: effects on children's participation, mental health, and psychosocial development. Occupational therapy in health care, 27(2), 99-112.
New York Times. (2013). Urinary Incontinence. Retrieved from http://www.nytimes.com/health/guides/symptoms/urinary-incontinence/risk-factors.html
Saab., J & Salvatore, S.P. (2015). Evaluating the cause of death in obese individuals: A ten-year medical autopsy study. Journal of Obesity, p. 1-7. Retrieved from https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jobe/2015/695374/cta/.
UCTV. (2014, May 14). The skinning on obesity: Generation XL [Video file]. Retrieved from http://www.uctv.tv/shows/The-Skinny-on-Obesity-Ep-5-Generation-XL-23719
UCTV. (2014, March 11). The skinny on obesity: An epidemic for every body [Video file]. Retrieved from http://www.uctv.tv/shows/The-Skinny-on-Obesity-Ep-1-An-Epidemic-for-Every-Body-23305
University of Maryland Medical Center. (2016). Urinary Tract Infections in Women. Retrieved from http://umm.edu/health/medical/altmed/condition/urinary-tract-infection-in-women