Common Bony and/or Articular Conditions
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, dislocation and history of fracture are factors which may lead to progressive loss of function and/or surgical intervention
Myositis Ossificans (MO) & Heterotopic Ossification (HO)
- Bone spontaneously lays down into muscle (MO) or in surrounding areas or joint space (HO) following blunt trauma or fracture
- Idiopathic onset associated with traumatic brain injury
- Presents as red, hot, swollen, marked painful motion
- Active and passive ROM is encouraged and may require spinting.
- MASSAGE, PASSIVE STRETCHING AND RESISTIVE EXERCISES ARE CONTRAINDICATED
Internal Derangement
- periodic locking of joint due to loose bodies in joint
- results in loss of end-range flexion and extension which gradually resolve; repeat occurrences and predispose OA changes
- in adolescents: associated with trauma (chip fracture) or osteochondrosis
- in adults: cartilage fractures due to trauma and becomes a loose body (treated with joint manipulation); may need arthroscopic removal
- in mid-age to elder: fragments are more numerous: may result in longer periods of limted motion
Subluxation of the Radial Head
- "Nursemaid's Elbow" or "Pulled Elbow": sudden traction injury
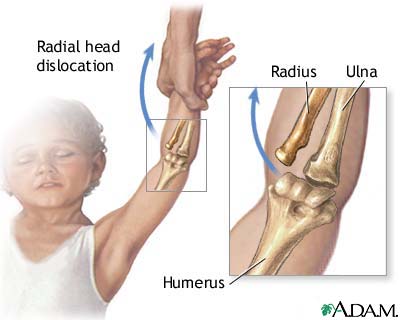
- Child is lifted up suddenly by the arm while it is held over their head in a pronated and extended position
- Presents with painful inability to use arm and avoidance of supination
- Generally resolves with short term immobilization
Trauma
- sprain/strain to joint capsule (likelihood increases with RA)
- traumatic ulnar dislocation
- fracture (radial fracture is most common elbow fracture)
- may result in post-immobilization capsular tightness and loss of motion, especially with closed reduction of a fracture
- may result in progressive osteoarthritis or joint replacement
- displaced fractures may require surgery with hardware and/or removal of bone
- should be taken with stretching if there is a bony block to ROM; overstretching can lead to hypermobility
Elbow Dislocation
Elbow subluxation and dislocation can have long-standing secondary effects associated with nerve trauma and heterotopic ossification. Uncontrolled swelling can result in disability that includes the wrist and hand.
Patients are typically placed in a posterior splint for up to 2 weeks and then begin gradual ROM and strengthening of surrounding structures to progressively add stability while ROM is progressively increased.