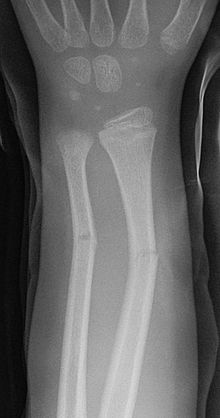
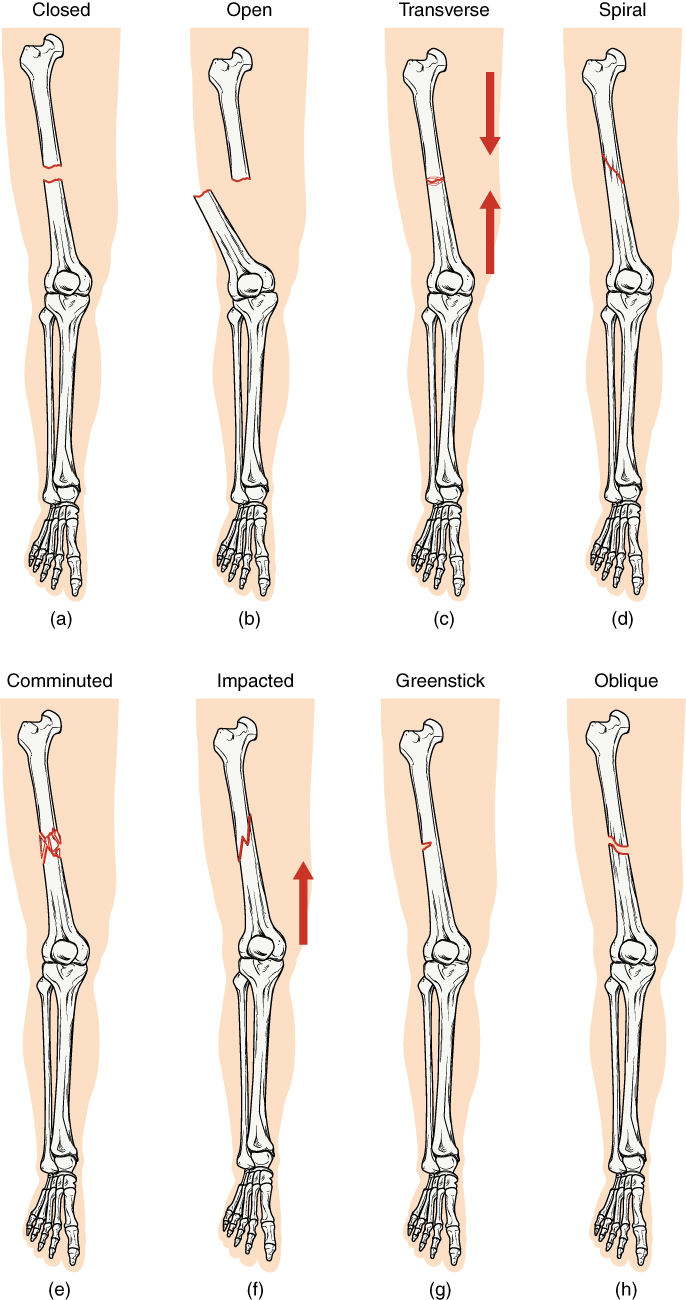
Fracture Types
The illustrations below provide examples of the major fracture presentations:
By OpenStax College [CC-BY-3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
From left to right, these radiographic images show a vertebral compression fracture, a calcaneus avulsion fracture, and a radial and ulna greenstick fractures
http://www.radpod.org/2007/01/27/gauchers-disease/
http://radpod.org/wp-content/uploads/2007/05/calcaneal_avulsion.jpg
Stress Fractures
- Most, but not all, stress fractures involve the lower extremity.
- Jumping, ballet, sports, marching, etc. common precipitating events.
- Common stress fracture sites:
calcaneus -- jumping
tibia/fibula -- running
patella -- hurdling
femur - change in distance or training surface in runners/walkers
pelvis, obturator ring -- gymnastics
ribs -- heavy lifting, coughing; first rib is most common site
vertebrae, pars interarticularis -- lifting
scapula, coracoid -- trap shooting
humerus. ulna -- throwing baseball, pitching
hamate -- golf, baseball
- Repetitive torsional (rotational) loading to the bone will typically result in a longitundinal-type fracture
- Can also be a secondary complication of an underlying pathology,metabolic impairments, such as post-radiation therapy bone loss, or medication side effects
http://www.radsource.us/clinic/0803
Pediatric Orthopedic Conditions
Pediatric conditions that affect bone tissue are acquired or congenital. Fracture on or near the growth place places the child at risk for disrupted bone growth.
Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease is an idiopathic necrosis of the femoral head, whichcan result in painful, limited motion and altered gait and increases risk for total joint replacement in adulthood. Note the change in femoral head shape below and its flattened appearance.
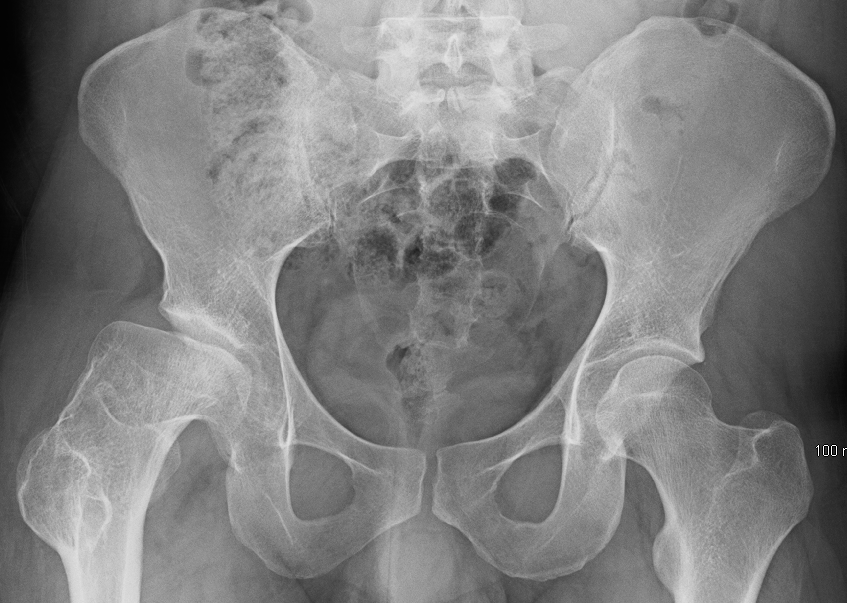
James Heilman, MD [CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)]
Osgood-Schlatter Disease can result when the tension forces on the quadricep results in a partial avulsion of the tibial tuberosity and produces secondary bone growth in the distal aspect of the tendon. Can be quite painful with any activities at that require strength/force from quadriceps, like running, jumping, and descending stairs. Generally resolves with conservative treatment and prescribedexercise.
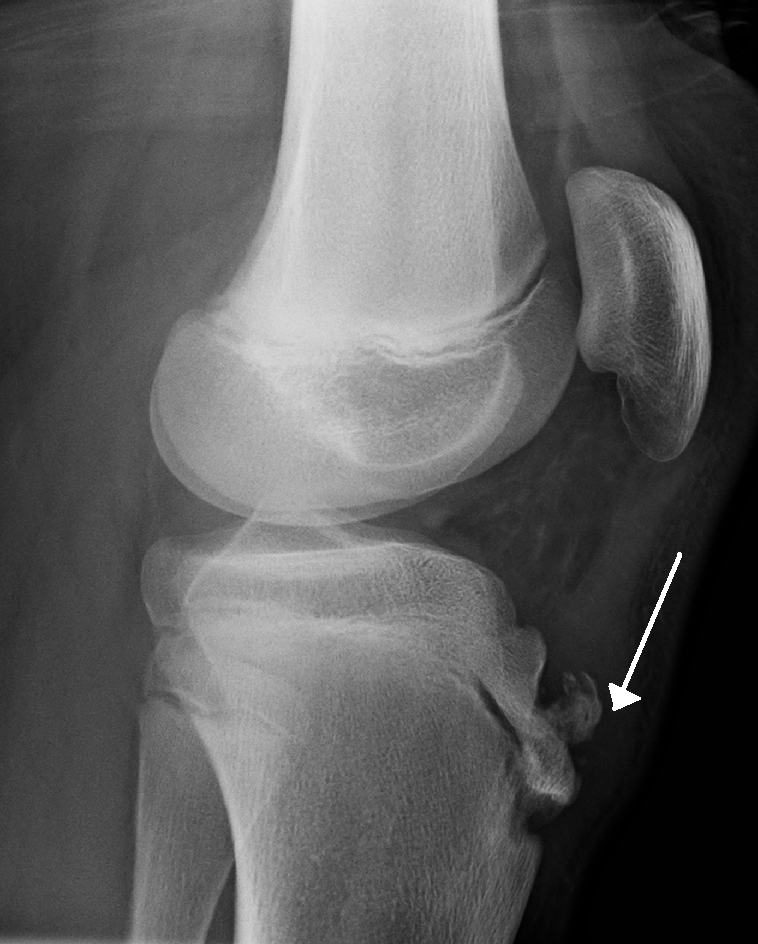
James Heilman, MD [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)]