Hand Function Review
-
Extrinsic and intrinsic muscles coordinate for optimal hand function
- wrist provides a stable base for the hand; distal carpal row (hamate, capitate, trapezoid, and trapezium) is the stabilizing segment
- as wrist position changes, functional length of finger musculature changes
- intrinsic muscles (within the hand) are interossei (from MCP to PIP-DIP on same digit) and lumbricals (originate from flexor digitorum profundus - insert on extensor expansion/hood)
- intrinsic muscle function is essential for fine motor control and a pinch grip
- At Home Study Guide
- Major functions include
- manipulation of objects
- fine motor control
- grip (prehension: power and precision)
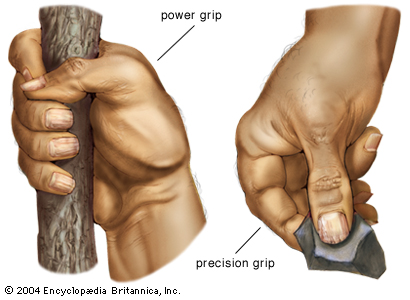
- 15 degrees of wrist extension is ideal for functional grasp
- sensory
- defense
- Length-tension relationships between opposing muscles, and joint and ligamentous stability determine effectiveness and efficiency in the hand
- Resting position of the hand facilitates preservation of length tension relationships during periods of immobility or neurological recovery