|
FN 225: Nutrition
Rathakette , Ph.D. Health Professions Division Lane Community College Eugene, Oregon
EXAM RESULTS-
The average for exam 3 was 38 points. Scores ranged from 20 to 47 FORUM for Week 8:
LECTURE
8
A
: Vitamins & Minerals- part 2
During Week 7, we looked at the first 4
NUTRICHARTS
:
During Week 8, we'll look at the last 2
NUTRICHARTS
.
NUTRI-CHART 5 lists the Nutrients Involved in FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE As discussed during Week 1, water is one of the 6 categories of nutrients. The others were
A pale yellow urine indicates that the body probably has enough water to accomplish these tasks. Am I Hydrated? Urine Color Chart.
|

| As the NUTRI-CHART says, sodium in the body helps with glucose transport in cells by being part of the sodium/potassium "pump". This "pump" helps keep the correct amount of water INside cells. Without this water, cells collapse and can't function.
Too much sodium in the body can contribute to hypertension if a person is among the perhaps 5% of people with hypertensionwho are salt sensitive, although some say the figure is higher. Sodium may cause calcium excretion in some people. Potassium helps keep the correct amount of water OUTside cells, by being part of the sodium/potassium "pump". Too little potassium in the body can be caused by abuse of what can be called the 3Ps.
Now watch "Video Clip 1: Electrolytes" below. |
| Video Clip 1: Electrolytes
approximately 8 minutes |
|
NUTRI-CHART
6
lists the Nutrients Involved in
BONE HEALTH.
As you can see at the top of this page, bone health depends on many factors, including
|

| The macronutrient protein is also important forstrong bones because
crystals
form around a
matrix
made of protein (collagen). High protein diets can promote calcium excretion as can the mineral sodium. Both protein and sodium are often high in American diets, which is not a good situation for bones, especially considering the diet might also be low in calcium.
Common American diets might also be low in 2 vitamins important for bones- vitamin D and vitamin K. (Remember that vitamin K is not the same thing as the mineral potassium, abbreviated with a K.) Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium and vitamin K helps make osteoclacin, a protein associated with bone matrix remodeling. |
| Video Clip 2: Bone Health Part 1
approximately 6 minutes |
|
The next Video Clip will help you fill in a remaining blanksin the phosphorus section
approximately 8 minutes |
|
There was a document posted in moodle that lists food sources of vitamins and minerals, including those that help with bones, such as calcium. Canned salmon is listed as a source of calcium, while fresh salmon is not listed. This is because the high heat used in the commercial canning process pulverizes the bones so they can be eaten. Some foods are fortified with bone-building nutrients, like the soy milk and orange juice shown below. 



|


The above display at a Smithsonian Museum in Washington D.C. (in the late 1980s) said:
Young animals must grow, and the length and size of bones must grow with them. Bone is a living substance. continually being eroded, reforming, and growing. Long bones, such as those in the legs of mammals, need a special way to increase their length. Each bone consists of a bony cap (epiphysis) and a long shaft (diaphysis). Between these is a layer of cartilage continually growing and being replaced by bone, thus lengthening the bone. The bone increases in diameter by deposition of bone on its outer surface and complementary erosion of bone on its inner surface.
This process is dependent upon vitamin A. |
|
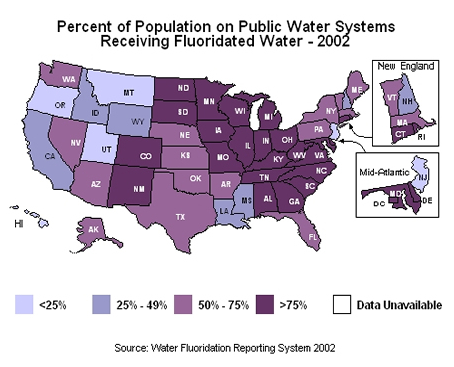
Fluoride is on the NUTRI-CHART for BONE HEALTH. For more information on fluoride, watch the last Video Clip.
Video Clip 4: Fluoride approximately 8 minutes |
|
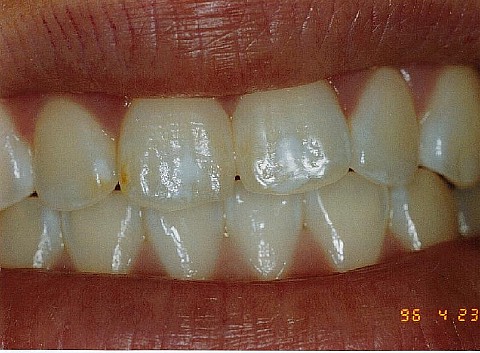
Fluorosis (white spots from too much fluoride) |