FORUM for Week 5:
- Take a look at the
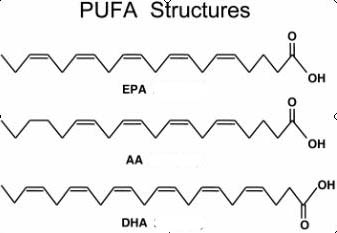
chart on page 64 of your packet called "Food Sources of Carbohydrates,
Lipids, Proteins". Now look at the food sources listed on that
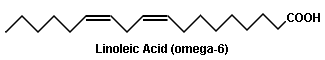
table of fatty acids, including SaFAs, MUFAs, omega 6 PUFAs,
short
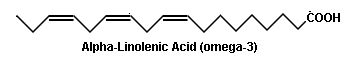
chain omega 3 PUFAs
and
long chain omega 3
PUFAs. What is ONE food you eat that is on any of
those lists of food sources of fatty acids and which
list (or lists) is it on?
(The chart on page 64 in your packet doesn't make this clear, but all foods with fat have a MIXTURE of fatty acids. So even though olive oil has MOSTLY MUFAs, olive oil also has SaFAs, omega 3 PUFAs as well as omega 6 PUFAs.)
- On pages 74 and 75 of your packet, read about some
recommended key words regarding lipids and health.
Consider Lou, who had triple bypass surgery at age 51.
Based on what you've learned this week, which of those recommendations do you think would be most important for Lou?
- Do you have any other questions regarding the lectures or the study questions for week 5?
LECTURE 5B:
Chapter 5: The Lipids: Fats, Oils, Phospholipids and Sterols
First look
through the major headings of this Lecture Outline in your packet:
Covered in Lecture 5A:
I
The THREE types (kinds) of LIPIDS
II Where
do
lipids
come from?
III Lipoproteins
IV Recommendations regarding lipids & heart health
III Lipoproteins
IV Recommendations regarding lipids & heart health
Now we're ready for:
V
Digestion and
Absorption
VI
Usefulness of
Fats
Before
continuing with this Lecture (and while you're waiting for the Video
Clips to buffer, go to the end of the Lecture
Outline in your packet (page 77) and answer those questions called
"REVIEW. QUARTET OF TRIOS" (with a fifth questions). I
suspect
you'll spend the most time on #4 and I'll
start a FORUM about it.
IV
Digestion and
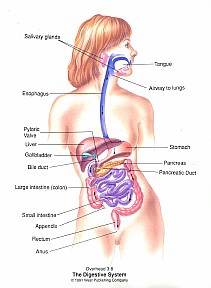
Absorption of Triglycerides(As mentioned before, triglycerides are the major type of lipid in food.)
As the
Lecture Outline in
your packet says, after you've eaten, a food, it quickly goes down to
your stomach where the fats are separated from the rest of the food.
As you'll see in the rest of this section, fats are difficult
to
digest so the body keeps them separated
&
isolated in the stomach while other parts pass
on
to the small intestine.
(You can click on the following image to see an enlarged version.)
Now watch the following Video Clip to continue with page 75 in your packet.
(You can click on the following image to see an enlarged version.)
Now watch the following Video Clip to continue with page 75 in your packet.