Since it's an example of an
communist country, Cuba's is an interesting statistic for Infant
Mortality Rate. Most Cuban
citizens live in poverty, with many factors contributing to this.
Some
feel one factor is the 70-year leadership of Fidel Castro.
Many others feel a factor is the United States Embargo Against Cuba, an economic, commercial, and financial embargo imposed on Cuba on February 7, 1962.
In February, 2008, Fidel turned over power to his brother, Raúl. Eduardo Machado, a Cuban playwright living in the United States, says "My hope is that Cuba is allowed to become a part of the world again while keeping the social reforms that the revolution is so proud of: free education for all and free health care."
Many others feel a factor is the United States Embargo Against Cuba, an economic, commercial, and financial embargo imposed on Cuba on February 7, 1962.
In February, 2008, Fidel turned over power to his brother, Raúl. Eduardo Machado, a Cuban playwright living in the United States, says "My hope is that Cuba is allowed to become a part of the world again while keeping the social reforms that the revolution is so proud of: free education for all and free health care."
Cuban
Exile
Ponders
Life After Castro, by Eduardo Machado, National
Public Radio, February 23, 2008.
Cuba limits
sales of food so all can eat, Associated
Press,
MSNBC, Oct. 10, 2008. "The lines are long and some foods are scarce,
but because the government has maintained and even increased rations in
some areas, Cubans who initially worried about getting enough to eat
now seem confident they won't go hungry despite the destruction of 30
percent of the island's crops by hurricanes Gustav and Ike last month."
Notes About IRAQ:
Notice that is the most
recent date on the above table is 2002,
which was before the 2003 U.S. invasion of Iraq. In 1990,
the
United
Nations
Security Council passed a
comprehensive ban on trade with Iraq. A devastating bombing
campaign
against Iraq in 1991 destroyed the country's civilian infrastructure
(leading to contaminated drinking water, lack
of
electricity
for hospitals
As of March 2003 (just prior to the war), between 1.7 and 2 million Iraqi civilians have died due to malnutrition and disease, about 700,000 of them are children.
Notice in the above table what happened to IMR in Iraq between 1990 and 2002.
This over 12-year embargo on Iraq was lifted in 2003 by the United Nations. I have not been able to find a current IMR for Iraq. Please let me know if you know anything about the current IMR in Iraq.
As of March 2003 (just prior to the war), between 1.7 and 2 million Iraqi civilians have died due to malnutrition and disease, about 700,000 of them are children.
Notice in the above table what happened to IMR in Iraq between 1990 and 2002.
This over 12-year embargo on Iraq was lifted in 2003 by the United Nations. I have not been able to find a current IMR for Iraq. Please let me know if you know anything about the current IMR in Iraq.
Now, go to the bottom of page 85 in your packet to the section about
B. Protein Deficiency: Global Hunger
Since the first cells to suffer from protein deficiency are those that are replaced most often, including red blood cells, plasma proteins as well as inner and outer skin cells, you would expect early symptoms to be problems affecting
blood
the digestive tract since it's inner "skin"
outer skin
Protein deficiency usually usually happens when
someone isn't
getting enough food, so that means they ALSO aren't getting enough
calories and they have something called PEM (it's also known as PCM).
There are two forms of PCM.the digestive tract since it's inner "skin"
outer skin
The
protein deficiency part is called kwashiorkor,
a
beautiful
word from Ghana in Africa that means "the evil
disease that strikes
the first
child when the second
child is born. In other words, weaning. It is
possible to
nurse 2 children, but it takes a well-nourished mother to do it.
When the child is weaned a mother who is very poor can probably manage just a thin cereal to feed her first child. The child may get barely enough calories, but not enough protein. That's the situation below for the child below who has kwashiorkor. Notice the edema (fluid buildup) at the ankles and wrists as well as the skin problems. I'll explain the edema in one of the Video Clips. On the right is the same child once protein was added to his diet.
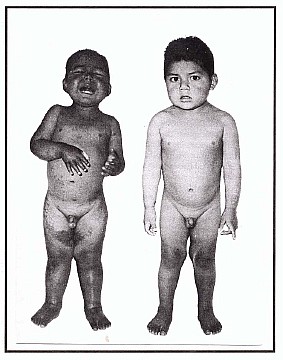
When the child is weaned a mother who is very poor can probably manage just a thin cereal to feed her first child. The child may get barely enough calories, but not enough protein. That's the situation below for the child below who has kwashiorkor. Notice the edema (fluid buildup) at the ankles and wrists as well as the skin problems. I'll explain the edema in one of the Video Clips. On the right is the same child once protein was added to his diet.

Sometimes
a person gets enough protein, but not enough calories. That
person has marasmus,
shown
below
with the girl with anorexia nervosa.


The mother and child shown below have BOTH a deficiency of calories and a deficiency of protein, so they both have PCM (PEM). Notice the abdominal edema (called ascites) in the child.

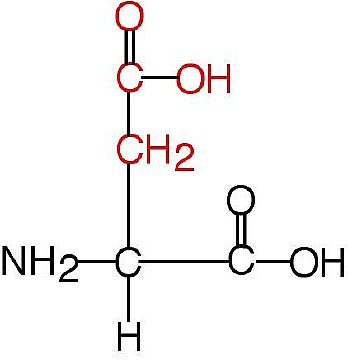
I Introduction
II The Structure of Amino Acids & Protein
III FUNCTIONS of Protein
on page 83 and 84.