V
Energy Use
What does
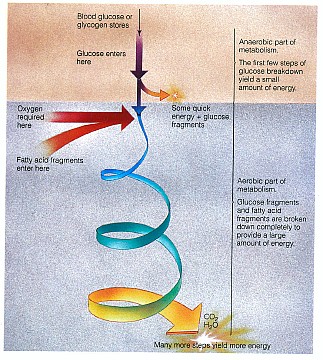
the purple arrow represent in the image below? _____________
What does the blue to green to yellow spiraled arrow represent? __________________
As time goes on, the rider is using more ________ than glycogen.
When does glycogen run out for this bike rider?
Two ways you can manipulate what you do to make glycogen last as long as possible is to:
Does it represent
glycolysis, or does it represent the Krebs cycle? If you're not
certain, check the FORUM for Week 10.
You
can click on the image if you want to see a larger version.
What does the blue to green to yellow spiraled arrow represent? __________________
Does it represent
glycolysis, or does it
represent the Krebs cycle? If you're not certain,
check the FORUM for Week 10.
VI
Fuel
Use
during AEROBIC
activity
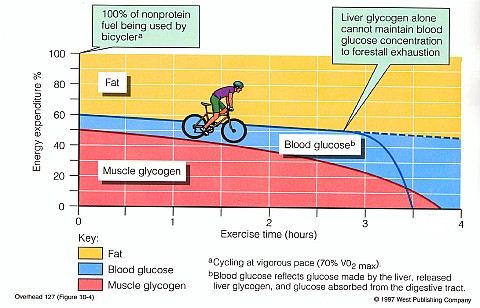
At the beginning of this bike ride, the rider is using
glycogen & fat, but slightly
more _________________.As time goes on, the rider is using more ________ than glycogen.
When does glycogen run out for this bike rider?
Two ways you can manipulate what you do to make glycogen last as long as possible is to:
- Train so you build up the number of
fat-burning enzymes you make. That means you can burn more
fat for energy, conserving glycogen for as long as possible.
- Eat plenty of whole foods with
carbohydrate so you have glucose to make glycogen.
VII
Fuel
Use
during ANAEROBIC
activity
Which part of step 5 is anaerobic? If you're still uncertain, watch the Video Clip again.
Anaerobic metabolism is almost entirely glycogen (as well as glucose in the blood) because burning fat requires oxygen.
You should be able to fill these in from the Video Clip.
Lactic
acid is produced when there's not enough __________________
in cells.
Ketones are produced when there's not enough __________________ in cells.
Ketones are produced when there's not enough __________________ in cells.
VIII
Protein as Fuel
X Sports Drinks
Protein
supplies
10%
of the fuel used during rest & activity.
A person needs extra protein in diet only if they are regularly exercise longer than 1 hour/day.
If you are an athlete, the extra protein is mainly needed to build and maintain muscle and other lean tissue.
IX
Fluids and TemperatureA person needs extra protein in diet only if they are regularly exercise longer than 1 hour/day.
If you are an athlete, the extra protein is mainly needed to build and maintain muscle and other lean tissue.
Sweat
helps
protect
you from overheating because it absorbs a lot of heat
before it changes from a liquid to a gas (evaporation).
Your packet has a chart comparing
Heat EXHAUSTION and
Heat STROKE
Heat STROKE is more dangerous because the high temperature can denature body proteins, which can lead to loss of brain function and death.
Your packet has a chart comparing
Heat EXHAUSTION and
Heat STROKE
Heat STROKE is more dangerous because the high temperature can denature body proteins, which can lead to loss of brain function and death.
X Sports Drinks
Water is all you need if
exercising less than about one hour.
Caffeine initiates release of fat into blood so muscles can use it for energy.
Side Effects: stomach upset- nervousness, irritability, headaches & diarrhea.
Advantages of warm-up- also stimulates release of fat into blood to be used by muscles, and it also warms the muscles to ready them for exercise.
What sports drinks offer besides fluid, to those exercising over one hour:
Homemade sports drink: 1 qt. water, 1 cup sugar-sweetened fruit juice, 1/3 tsp. salt
On another note.......

Last summer I tried growing teosinte, which is thought to be a relative of what wild corn looked like over 10,000 years ago before corn was domesticated. Controversy 12 in the text speaks of that corn.


Caffeine initiates release of fat into blood so muscles can use it for energy.
Side Effects: stomach upset- nervousness, irritability, headaches & diarrhea.
Advantages of warm-up- also stimulates release of fat into blood to be used by muscles, and it also warms the muscles to ready them for exercise.
What sports drinks offer besides fluid, to those exercising over one hour:
- Electrolytes like sodium- may accelerate glucose & water absorption from digestive tract. About 225 mg per 12 oz. (150 mg per cup) is enough.
- Glucose: no more than 7%, which is about 23 grams per 12 oz. (15 grams per 1 cup). More sugar than that delays fluid going from the stomach to the small intestine where it can be absorbed.
- Psychological edge
- Taste
Homemade sports drink: 1 qt. water, 1 cup sugar-sweetened fruit juice, 1/3 tsp. salt
On another note.......

Last summer I tried growing teosinte, which is thought to be a relative of what wild corn looked like over 10,000 years ago before corn was domesticated. Controversy 12 in the text speaks of that corn.


END of Lecture 10A