|
A. Value of Fats in
the Body
(another
section will look at the value of fats in
the diet)
1. FUNCTION
of triglycerides
and fatty acids in the human
body
Similac
Advance Baby formula: Nonfat milk, lactose,
high-oleic safflower oil, soy oil, coconut
oil, whey protein concentrate plus small
amounts of C. and about 30
added vitamins and
minerals
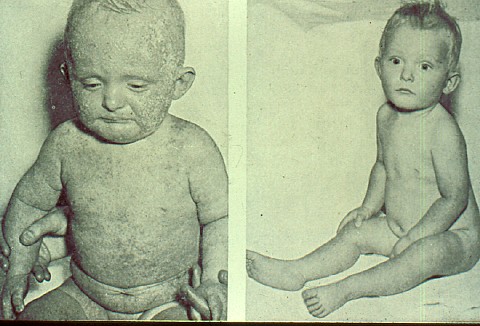
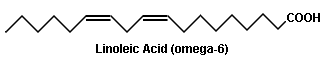
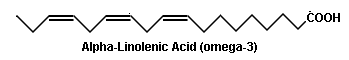
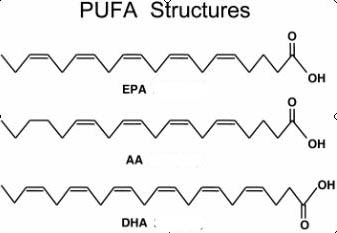
This formula has many different kinds of oil in an attempt to match the various types of fatty acids in human milk.
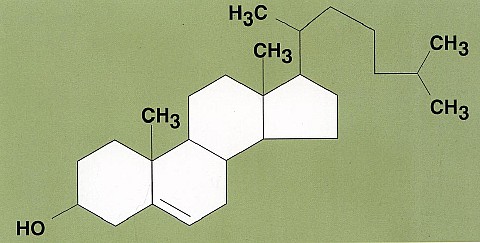
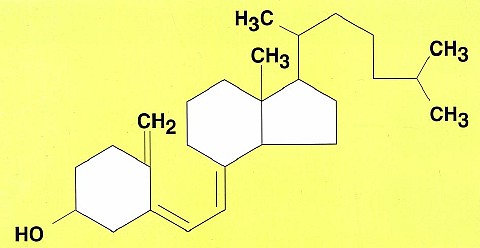
2. FUNCTION
of cholesterol
in human body
You
don't need cholesterol in the diet
for these 3 functions cholesterol in the
body because your body can synthesize
the cholesterol
it needs.
3. FUNCTION
of phospholipids in human
body. Phospholipids are part of the lipoproteins. They are EMULSIFIERS in cell membranes as well as in the blood What are the 3 places in the body where we've talked about emulsification taking place:
|