Overview of peripheral nerve injury and entrapment
Nerve entrapment in the upper and lower extremities can be temporary or long-standing. Conditions such as obesity and pregnancy where there is increase fluid or body weight on nerves can interfere with nerve gliding. Surgical interventions and subsequent scar formation can also entrap nerves, resulting in chronic nerve symptoms, pain, and loss of function.
In some cases, patients consent to surgery to release the nerve or to transfer nerves to restore function in affected sensory and motor areas.
Upper Extremity Peripheral Nerve Injuries
Upper extremity nerve injuries are more common than lower extremity. Compression and traction (stretching) forces to components of the brachial plexus can result in pain, loss of sensation, and loss of motor function. Note how the brachial plexus originates from C5-T1 and then forms a series of overlapping trunks, divisions, and cords, before branching into peripheral nerves. Proximal compression can result in significant neurovascular syndromes, which may requires surgical releases to preserve nerve function and circulation. Neal and Fields (2010) noted, "risk factors include a superficial position, a long course through an area at high risk for trauma, and a narrow path through a bony canal"
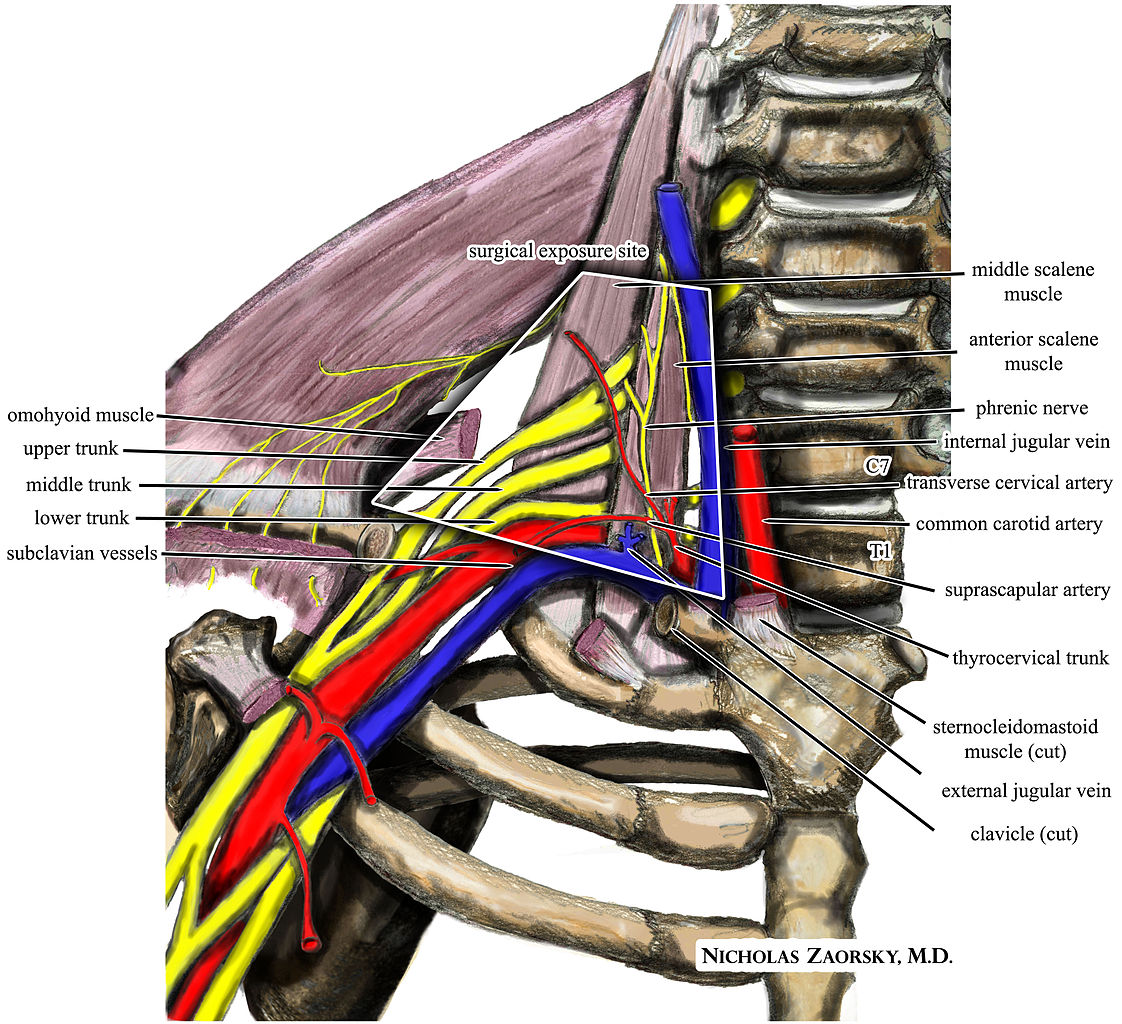
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Brachial_plexus_anterior_view_nerves.JPG;
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Wikipedia_medical_illustration_thoracic_outlet_syndrome_brachial_plexus_anatomy_with_labels.jpg
Upper Extremity Nerve Injury Signs and Symptoms
|
Nerve |
Injury Risk |
Presentation |
|
Axillary |
Stretch during abduction; glenohumeral dislocation; compression in axilla (e.g. misuse of crutches) |
Weakness in teres minor and deltoid |
|
Long Thoracic |
Sudden upper extremity traction; shoulder depression with contralateral lateral cervical flexion, sustained compression ("Backpacker's syndrome) |
scapular winging |
|
Throwing athletes, trauma, clavicle fracture |
supraspinatus weakness, atrophy and tenderness, pain with horizontal adduction, |
|
|
Median |
Elbow, forearm, and wrist overuse or injury |
weak and painful grip; sensory changes in hand |
|
Musculocutaneous |
Shoulder dislocation; biceps injury; hypertrophy of coracobrachialis |
shoulder and elbow flexion weakness |
|
Radial |
Proximal humerus fracture; elbow fracture or dislocation; "Saturday Night Palsy" when passing out from alcohol use results in prolonged compression on chair or bar |
weakness in elbow flexion and wrist extension |
|
Ulnar |
Elbow dislocation or prolonged posterior elbow compression; repetitive throwing |
weakness in the ulnar side of the hand and interossei |
Lower Extremity Nerve Entrapment Signs and Symptoms
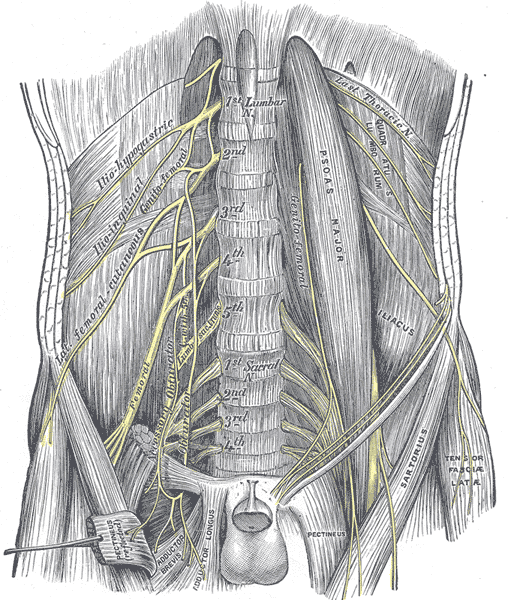
|
Nerve |
Injury Risk |
Presentation |
|
ilioinguinal (T12-L1)
|
Lower abdominal surgery; orthopedic surgery (iliac bone harvesting for bone graft), pregnancy
|
pain in groin and medial inner thigh, may radiate to genital areas |
|
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (L1-L3) |
tight clothing (e.g. jeans), pregnancy, trauma to ASIS |
also known as "meralgia paresthetica" burning, coldness, or lightning like pain on lateral thigh
|
|
femoral nerve (L2-4) |
trauma (surgical or other), pelvic fracture, acute hyperextension of hip, diabetes (neuropathy), tumors |
numbness, tingling and burning in the thigh, quadriceps weakness; difficulty managing stairs, feeling like knee will buckle |
|
sciatic nerve (L4-S1)
|
hypertrophy of piriformis, direct trauma to SI or gluteals, hip flexion contracture, excessive hamstring exercise
|
also known as "piriformis syndrome" Numbness, tingling, and weakness in the posterior hip and extend down posteriorly to the toes |
|
tibial nerve
|
Rheumatoid arthritis, Baker's cyst (posterior knee), diabetes, tight-fitting shoes, pronation or pes planus
|
also known as "tarsal tunnel syndrome" when involves the posterior tibial nerve sensation changes and weakness to the bottom of the foot and toes; weakness in plantar flexion and eversion; pain with weight bearing
|
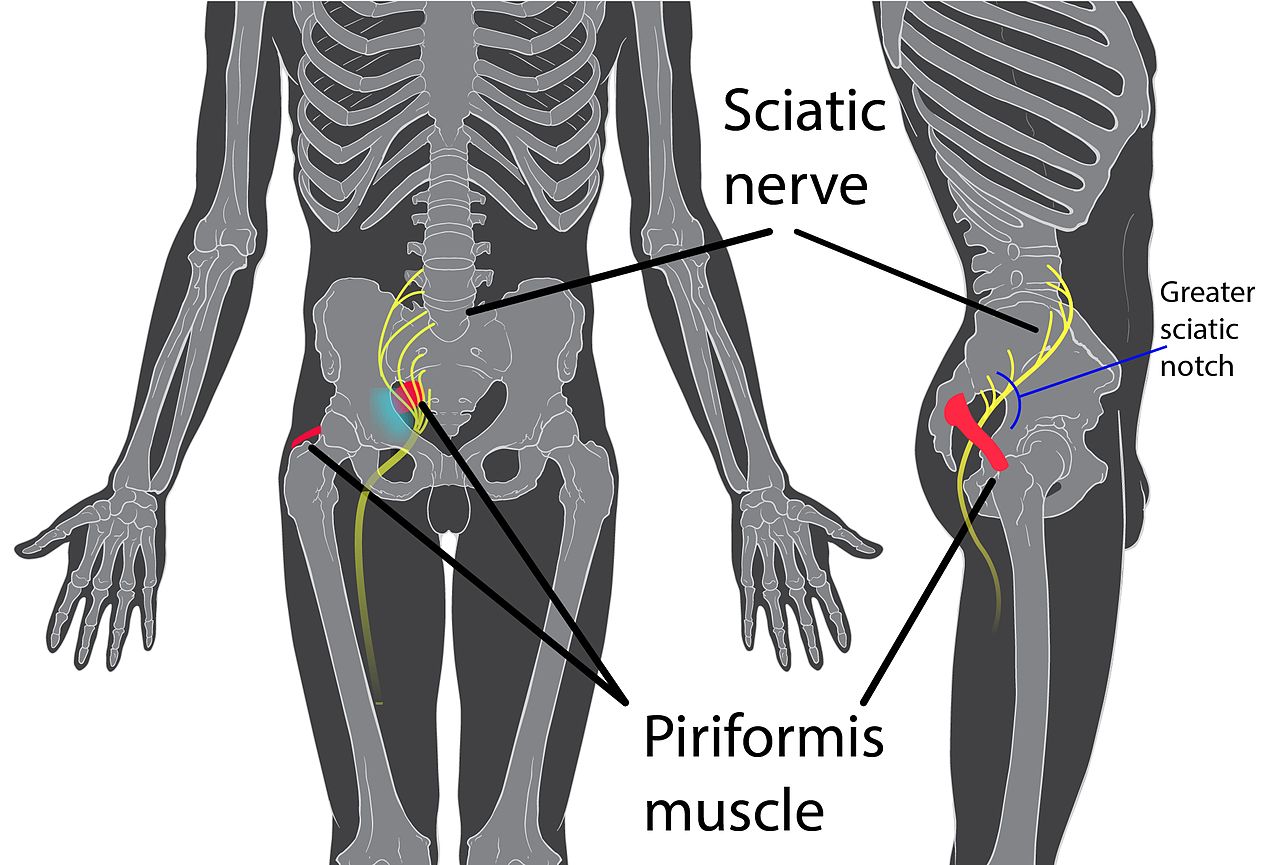
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piriformis_syndrome