Introduction
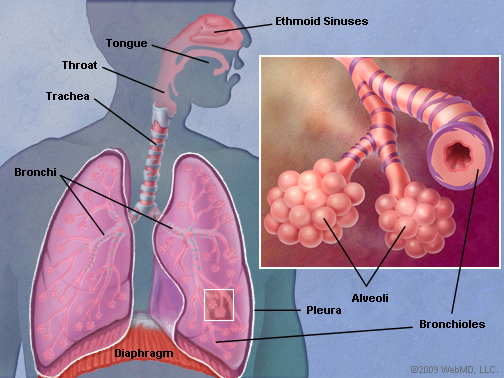
Understanding function of the pulmonary system is essential for safe and effective exercise selection and planning.
Pulmonary dysfunction is encountered acidosis the life span and is significantly influenced by environmental and personal factors. Regardless of age, decreased breathing efficiency and effectiveness results in decreased activity tolerance and can limit full participation in work, home, and school activities.
Although industrial safety standards have improved and tobacco use is declining, there are several generations of clientele with decreased lung function as a result of one or often both of these exposure points.
Optimal care and safe discharge planning often involves close coordination with nursing, Respiratory Care, and family. Treatment progression and discharge planning may include the use of supportive equipment, such as breathing apparatus and supplemental O2 , instruction therapeutic positioning and postural control, breathing reeducation, and progressive reconditioning
Smoking decreases overall health, with primary effects on the cardiopulmonary system. In addition to implementing the PT plan of care, PTAs are also health advocates and communicate effectively with patients in health promotion and disease prevention.
Lesson Objectives
- Define ventilation and perfusion
- Identify primary and secondary muscles of inspiration and exhalation
- Describe signs and symptoms of pulmonary and respiratory dysfunction.
- Compare and contrast obstructive with restrictive lung disease.
- Describe pre-and post-operative risk factors associated with disorders of the respiratory system.
- Explain how impaired lung function affects exercise tolerance.
- Describe guidelines for stopping an exercise test/activity.
- Select relevant test and measurement methods associated with interventions to reduce impairments in ventilation and respiration:
- Observation: sitting preference, characteristics of digits (cyanotic, nicotine-stained, use of supportive devices (AD, oxygen)
- Anthropometric characteristics: chest shape and body type
- Thoracic/spinal ROM Chest mobility/palpation
- Pain
- Posture
- Pulse oximetry
- Breathing patterns and breath sounds (auscultation: normal and abnormal)
- Cough efficiency and effectiveness
- Exercise and pulmonary function testing (baseline or repeat measures)
- Recognize and report normal and abnormal values (lung volumes, spirometry, pulse oximetry, arterial blood gas).
- Describe the significance of cyanosis, hypoxia, and hypercapnia as it relates to activity tolerance.
- Describe the continuum of assisted mechanical ventilation (02, ventilators).
- Select appropriate interventions to reduce impairments associated with pulmonary dysfunction for selected case simulations
- airway clearance (postural drainage, autogenic drainage, coughing, mechanical devices, manual techniques).
- therapeutic exercises for inspiratory muscle training and optimal gas exchange (diaphragmatic, segmental, pursed lip).
- energy conservation and pacing.
- positioning and postural training.
- Select documentation elements that demonstrate skilled and medically necessary care and coordination with the supervising PT in simulated pulmonary cases
- Consider psychosocial and environmental contributors during clinical decision making and patient instruction in simulated pulmonary cases
Connecting Reading to Learning Objectives
