Breathing Measures
Reading and Web Exploration
- Cameron & Monroe, Chapter 24, 368-376 (to Intervention)
- This resource provides information on a measurement device used at times by respiratory therapists to measure how you push air out of your lungs (American Lung Association, 2018). I have seen these on occasion when working with patients with a pulmonary health condition (2018).
Breathing Patterns
Breathing pattern is documented in terms of rate, regularity, and location
|
Normal Rate (Adults) |
Inspiration:Expiration (Normal) |
Inhalation:Expiration (Obstructive) |
|
12-20/min > 20/min is tachypnea <12 is bradypnea |
1:2 |
1:4 |
Apnea - cessation of expiration; no airflow in or out of lungs. May be voluntary or involuntary. Prolonged apnea results in CO2 accumulation and triggers a healthy nervous system to increase arousal and breathing.
Tachypnea - shallow and rapid breathing, often present at rest with pulmonary and systemic infection
Bradypnea - shallow and slow breathing, present in coma, increased intracranial pressure
Dyspnea - labored breathing, shortness of breath
Orthopnea - difficulty breathing in supine; often experienced with obesity and lung disease
Hyperventilation - rapid and deep breathing, triggered by increased CO2 ; also associated with pain, anxiety, asthma/obstructive lung disease, heart failure; Associated symptoms include dizziness, distal muscle cramping, weakness, syncope
Cyanosis - bluish appearance in nail beds or lips; sign of inadequate ventilation and perfusion

Image of cyanosis
Retrieved from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Blue_finger_tips_3.jpg
Shallow, deep, rapid, irregular, asymmetric are all qualitative observational terms to describe breathing patterns.
Breathing motion is assessed by palpation of the thoracic at upper, mid, and regions; motion is also assessed holistically based on the overall automatic pattern. Accessory muscle palpation provides qualitative information about muscle tone and activation during breathing at rest.
- diaphragmatic: often referred to as "belly breathing"; diaphragm is the primary muscle used in inhalation; abdomen rises and falls and chest wall is relatively still
- upper chest: shoulders and sternum rise and fall when initiating inhalation; indicates use of accessory muscles at rest
- paradoxical: upper chest rises and diaphragm pulls in during inhalation and pushes abdomen out during exhalation; typically associated with acute pneumothorax or palsy
Posture and Body Type
- Forward bend
- "professorial"
- cachectic (thin) - suggests high energy cost for breathing
- obese - increased risk for positional lung restriction and decreased endurance
- congential abnormalities
- pectus carinatum
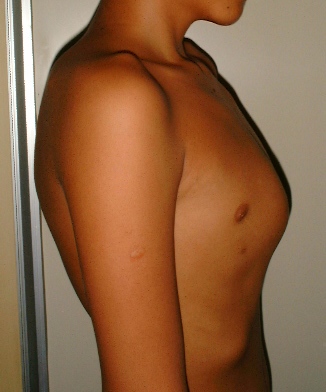
By Jprealini (Own work) [GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) or CC BY-SA 4.0-3.0-2.5-2.0-1.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0-3.0-2.5-2.0-1.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
- pectus excavatum
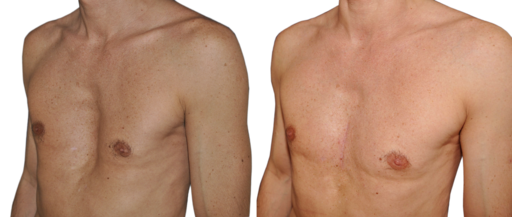
By Cchavoin (Own work) [CC BY-SA 4.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
- idiopathic scoliosis
- spinal curvature: kyphosis, scoliosis
Equipment Pulse Oximetry
Observation include noting the use of supplemental oxygen and flow rate or other devices to support breathing function during activity
Pulse oximetry measures oxygen saturation and is used to guide activity intensity and inform responsiveness of interventions to improve gas exchange. Normal values are 95%-100% (Cameron & Monroe, 2011).
Breath Sounds
- Web exploration: Physiological and pathological breath sounds
An excellent resource to explore breath sounds.
- Points of auscultation
- Use of a stethoscope; direct patient to breath deeply in and out with mouth open
- Normal
- Tracheal
- Vesicular
- Bronchial
- Bronchovesicular
- Adventitious or not normal - when a breath sound is heard in an unexpected region or creates dissonance (bad sound)
- Crackles (rales)
- Wheezes (rhonchi)
- Stridor
- Stertor
- Gurgling
Percussion
- This technique is performed as a means to assess lung density during physical assessment
- Thoracic findings are largely documented as normal, dull (indicating increased density/less air), or tympanic (hollow, indicating more air)
- Literature suggests mixed findings for percussion as reliable in detecting evidence of lung disease when compared to radiographic imaging (Wipf, et al., 1999)
Standardized Assessments
PTs and PTAs use standardized assessment to monitor response to exercise. Common standardized assessments used in this population include:
- Dyspnea index
- Rate of Perceived Exertion
- Six Minute Walk Test
References
Wipf, J. E., Lipsky, B. A., Hirschmann, J. V., Boyko, E. J., Takasugi, J., Peugeot, R. L., & Davis, C. L. (1999). Diagnosing pneumonia by physical examination: relevant or relic?. Archives of Internal Medicine, 159(10), 1082-1087.


