Types of Neurons
Peripheral nervous system image is of a sensory and afferent: action potentials toward CNS
•Functional classification
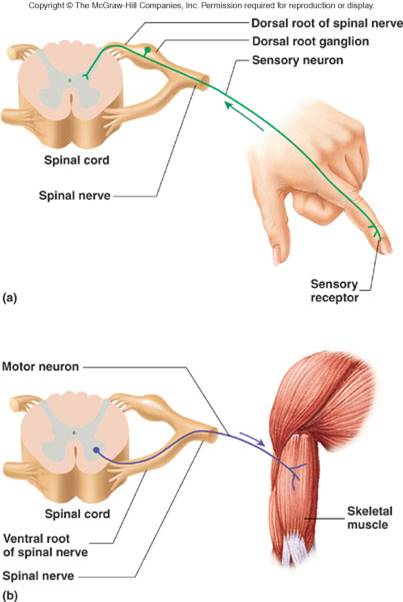
- Sensory or afferent: action potentials toward CNS sensory receptor see above
- Motor or efferent: action potentials away from CNS - spinal cord to muscle for example
- Interneurons or association neurons: within CNS from one neuron to another
•Structural classification
- Multipolar: most neurons in CNS; motor neurons
- Unipolar: single process that divides into two branches. Part that extends to the periphery has dendrite-like sensory receptors
PNS/Peripheral Nervous System Goodman Reading Summary
PNS/Peripheral Nervous System Goodman Reading Summary Guided Learning 12 min
Divisions of PNS/Peripheral Nervous System
Most nerves contain a mixture of neurons
- Includes motor, sensory, neurons of the somatic nervous systems and autonomic nervous system (ANS) which includes sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons
Afferent pathways: sensory responses from the periphery (touch, position, pain)
Efferent pathways: motor responses from the center/spinal cord to the periphery
- Includes somatic motor nerves that innervate skeletal muscles
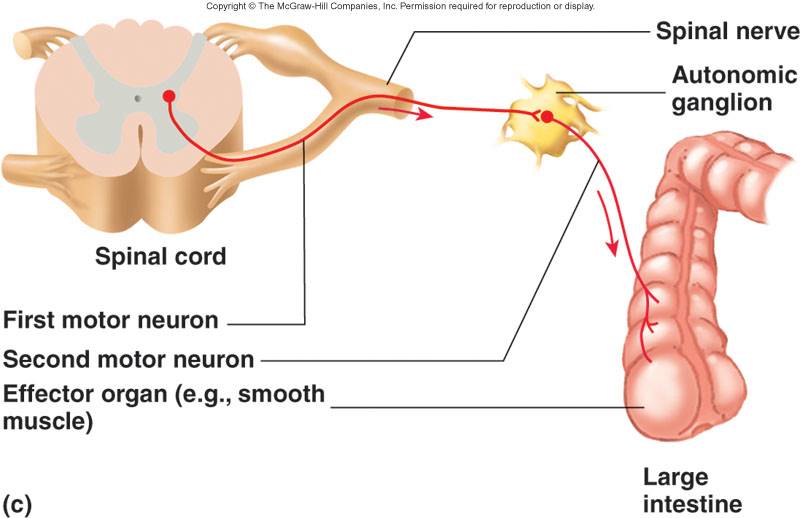
Autonomic nervous system (ANS):
Organs receive dual innervations from both sympathetic and parasympathetic branches to maintain homeostasis
Divisions of ANS
- Sympathetic. Prepares body for physical activity such as fight or flight response.
- Sympathetic (thoracolumbar)
- Parasympathetic. Rest, relax, digest, eliminate
- Regulates resting or vegetative functions such as digesting food/esophagus, stomach, intestines or emptying of the urinary bladder.
- Enteric. plexuses within the wall of the digestive tract. Can control the digestive tract independently of the CNS, but still considered part of ANS because of the parasympathetic and sympathetic neurons that contribute to the plexi.
Connection between the PNS and ANS broken down.
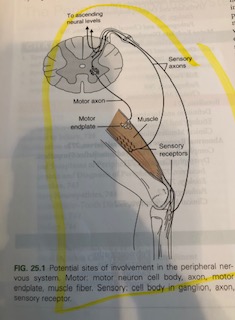
Take home message:Example: If while chewing/digesting an orange (ANS/parasympathetic branch), I receive a stimulus such as noxious heat from a stove to my finger/part of the peripheral nervous system, a response occurs involving sensory receptors (heat to my fingers) and a motor response (motor axon to motor endplate) when I pull my finger off of the stove. In the meantime my ANS is stimulated specifically the parasympathetic branch, and my digestion stops because my ANS and PNS communicate and right now the focus is getting my finger away from the noxious heat/stove!
Neuronal Communication
Image is of a neuron that is excited and communicating with other neurons!
- Cells produce electrical signals called action potentials.
- Action potential provide the transfer of information from one part of the body to another part of the body.
- Electrical properties result from ionic concentration differences across the plasma membrane and the permeability of the membrane.
Peripheral Nervous System and Age-Related Changes

Image is of an older adult
Decreased sensory receptors on skin
- Increased skin injury
- Slowing of action potential propagation
- Decreased neurons, decreased neurotransmitter receptors, decreased speed of transmission
- Decreased autonomic sensory function
ANS Parasympathetic Responses: Changes in Bowel/bladder, BP regulation, H20 regulation
.