Genitourinary Diseases and Conditions
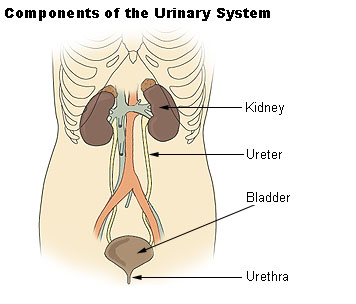
Urinary System
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Illu_urinary_system.jpg
Anatomy
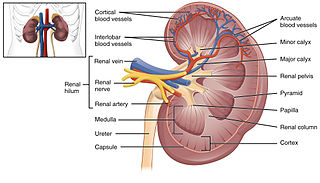
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/87/2610_The_Kidney.jpg/320px-2610_The_Kidney.jpg
- Primary components
- Kidneys
- Ureter
- Bladder
- Urethra
- Secondary Components
- Prostate
- Pelvic Floor Muscles
- Genitals
Physiology
Fluids are filtered through the kidneys and the filtrate is converted to urine. Urine is mostly water and urea, which is a metabolic by-product of protein metabolism, and electrolytes
Urination is mediated by voluntary and involuntary nervous system actions:
- L1-L3 forms the sympathetic branch
- S2-S4 forms the parasympathetic branch - visceral and afferent pathways
Selected GU Medical Terminology
- Dysuria = abnormal urine/urination. Incontinence is a form of dysuria
- Incontinence = involuntary loss of urine. Incontinence can be
- urge - sensation of needing to urinate - overactive
- stress - muscular insufficiency
- overflow - insufficient bladder emptying or urethra blockage
- functional - unable to find/get to the toilet in time
- Enuresis= involuntary voiding during sleep
- Voiding =emptying urine from bladder
- Micturition = urination: good interactive activity with graded quiz found here Link to animation of the micturition reflex
- Hematuria = blood in urine
- Pyuria = presence of pus/bacterial infection in urine
- Urgency = sensation of need to urinate, may be neurological or due to a spasm of smooth muscle in the bladder
Pathology Overview
- Urinary Tract Infection UTI = bacterial infection
- Uretritis=inflammation of the urethra
- Cystitis= inflammation of the bladder
- Pyelonephritis = bacterial infection of the kidneys
- Nephrolithiasis= kidney stones composed of minerals and salts
- Cystocele= fallen bladder
- Neurogenic bladder = dysfunctional autonomic control of the micturition
- Benign prostate hypertrophy or dysplasia BPH= enlargement of the prostate gland (American Urology Assn, 2019)
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Overview
- Increased risk with catheterization
- Increased risk with hospitalization
- Higher risk if a medical history of UTI's is present
- Higher incidence with individuals with diabetes and women.
- women have a shorter urinary tract which increases the risk (NYT, 2013)
- Most common cause is E Coli bacterial infection
- If untreated can lead to kidney infection and sepsis/septic shock
Signs and Symptoms
- Frequency of urination/urinary urgency
- Painful urination
- More common in men with UTI's than women with UTI's which is one of the reasons why UTI's are under diagnosed in women
- Burning feeling in the bladder
- Confusion
- Milky or cloudy urine
- Blood in urine
- Fever
- LBP
Uretritis and Cystitis
- Associated with sexually transmitted disease (STD)
- Signs and symptoms include increased frequency and urinary urgency
- Supra pubic pain, foul smelling urine, pyuria
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria, fatigue, anorexia, cognitive changes
- Results in pain, swelling of involved structure
- Treated with antibiotics and education/nursing care
Pyelonephritis

Medical News Today|1100 × 734 jpeg
- Acute or chronic inflammation of renal pelvis, or parenchyma of kidney
- Infection ascends from lower urinary tract.
- Often pre-existing factor = hx of UTI's and or Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
- Signs and symptoms: mild sluggishness, s/sx cystitis, fever, chills, vomiting, malaise, severe flank pain, costovertebral tenderness on affected side
- Bacteriemia, septic shock
- Chronic pyelonephritis starts in medulla of kidney spreads to cortex.
Nephrolithiasis
- Problem primarily associated with the kidneys
- Kidney stones: crystallization of calcium, uric acid, magnesium-ammonium acetate
- Stones may form anywhere along the urinary tract
- Stone formation is associated with decreased fluid intake, low urine volume, genetic factors, bed rest and sedentary lifestyle
- Higher risk in areas of hot temperatures and high humidity
- S/sx similar to pyelonephritis marked increase in flank pain and urination pain

https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Blausen_0595_KidneyStones.png
Renal Trauma

Blunt trauma to the kidneys can occur in a bike accident
- Blunt trauma: car, bicycle accidents, sports injuries, falls with injury to flank, abdomen or back
- Penetrating gun shot and/or stab wounds
- Renal trauma is diagnosed using ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, recent history, hematuria, intravenous pyelogram/IVP.
Psychosocial affects of Urinary Incontinence
- contributes to avoiding social activities, travel
- contributes to avoiding sexual encounters
Patient Support Equipment for Medical Management of Incontinence
-
Urethral catheters - tube placed in bladder via urethra
- Ureteral catheters - tube between kidney and urethra
- Supra pubic catheters -tube placed directly into superior aspect of bladder
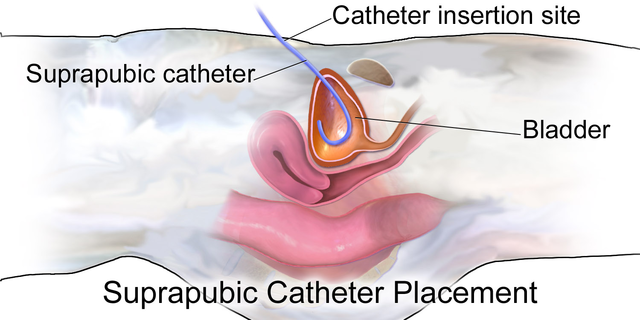

- Nephrostomy tubes

- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nephrostomy
- Intermittent catheterization
Incontinence pads - these products are progressively improving to help support dignity and function

