Key Terms
- Static - when the body is at rest, or still
- Dynamic - when the body or body segments are moving (e.g. during a functional activity)
- Base of Support (BOS)- area of the body in contact with the supporting surface
- Postural control - ability to maintain stability in a particular context (i.e., environment). For example, sitting on a stool vs. sitting on a standard chair requires different postural control in the trunk
- Center of Gravity (COG) - a single point in the body which represents where the entire weight of the object is centered; the point at which all parts of the body balance each other. The COG will change based upon positional changes.
- Limit of Stability (LOS) - the greatest distance in any direction a person can lean away from a midline vertical position without falling, stepping, or reaching for support.
 http://nothings.livejournal.com/222931.html
http://nothings.livejournal.com/222931.html
- Neutral posture - COG is positioned over BOS
- Poor posture - strain to body parts resulting from inefficient balance over BOS
- Line of gravity (LOG) - vertical line positioned through the body's COG. Also referred to as the Vertical Gravity Line (VGL)
- Anatomical position - universal reference position or anatomical planes
- REVIEW and be prepared to CORRECTLY IDENTIFY the general anatomical reference points below
- anterior
- posterior
- dorsal
- ventral
- palmar/plantar
- medial
- lateral
- proximal
- distal
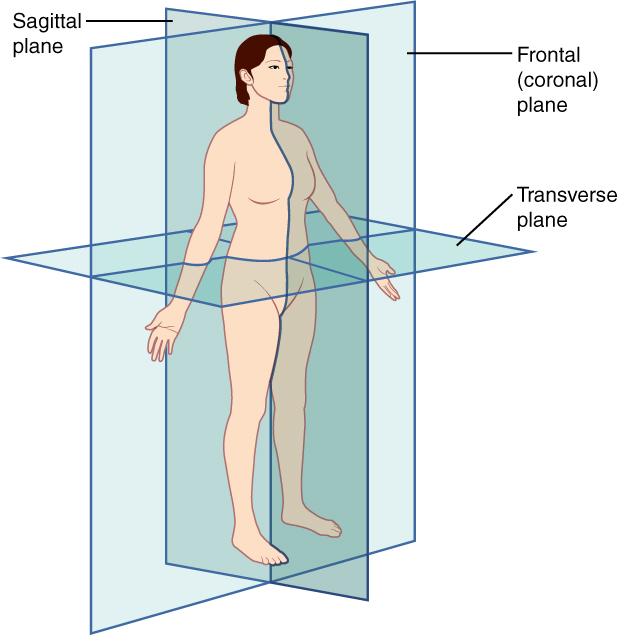
- sagittal
- frontal
- transverse
- cephalad/superior
- caudad/inferior
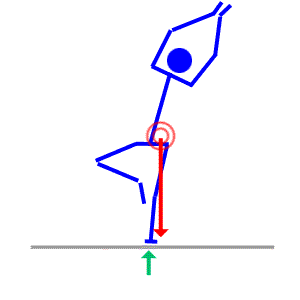
- Ground reaction force (GRF) - Force exerted back on the body by the ground
- Lordosis - inward curve at spine (normal resting position of cervical and lumbar segments)
- Kyphosis - outward curve at spine (normal resting position of the thoracic segments)
- Scoliosis
toc | return to top | previous page | next page