Three Major Types of Current Used in Electrical Stimulation (estim)
Approximately 6 minutes
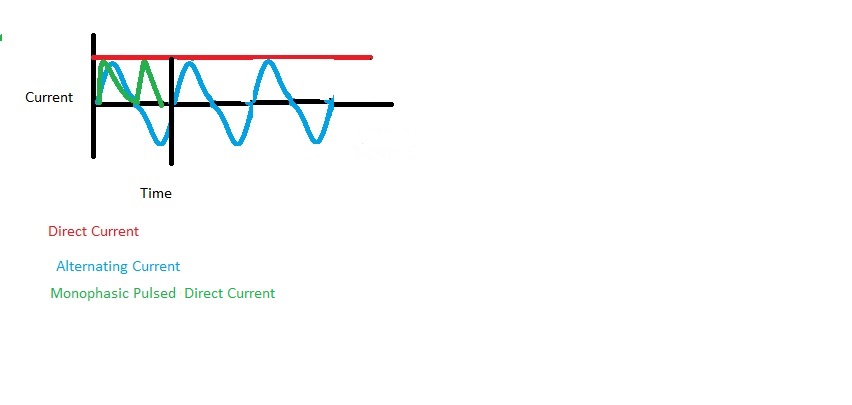
There are three basic waveforms used in commercial therapeutic electrical stimulation units: direct current, alternating current, and pulsed current.
Direct Current (DC) - Galvanic
- Continuous unidirectional flow of charged particles with a duration of at least 1 second.
- One electrode is always the anode (+) and one is always the cathode (-) for the entire event.
- There is a build-up of charge since it is moving in one direction causing a strong chemical effect on the tissue under the electrode
- Most commonly used for wound care and with iontophoresis
- Iontophoresis and microcurrent are clinical examples of direct current interventions
- Note : Monophasic also refers to direct current, but it is interrupted and not continuous (i.e., pulsed), so the chemical effect is minimal
Alternating Current (AC) - Biphasic
- Uninterrupted, bidirectional flow of ions; direction changes at least once per second.
- Frequency - the rate at which the current switches direction
- Electrodes continuously alternate their polarity each cycle, therefore no build-up of charge under the electrodes
- Types of modulated AC current used on biological tissue
- Burst-modulated - known as "Russian" current
- Amplitude-modulated - known as interferential current
Pulsed Current (pulsed - AC and DC)
- Flow of charged particles stops periodically for less than 1 second before the next event
- Pulses can occur individually or in a series
- Monophasic pulses do not alternate; pulsed monophasic (travels in one direction) current allows for a charge to accumulate in biological tissue
toc | return to top | previous page | next page