Types of Neurons
•Functional classification
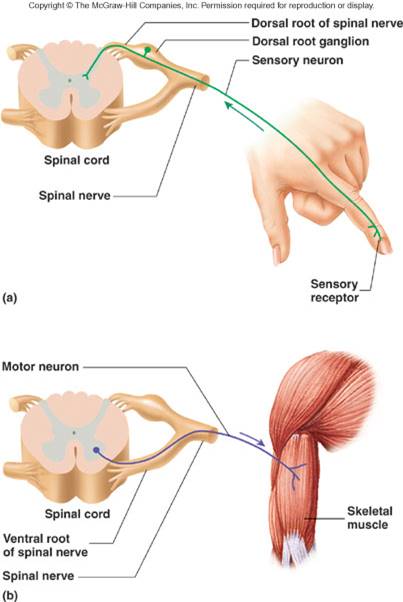
–Sensory or afferent: action potentials toward CNS (sensory receptor see above)
–Motor or efferent: action potentials away from CNS - spinal cord to muscle for example
–Interneurons or association neurons: within CNS from one neuron to another
•Structural classification
–Multipolar: most neurons in CNS; motor neurons
–Unipolar: single process that divides into two branches. Part that extends to the periphery has dendrite-like sensory receptors
Motor Division of PNS/Peripheral Nervous System
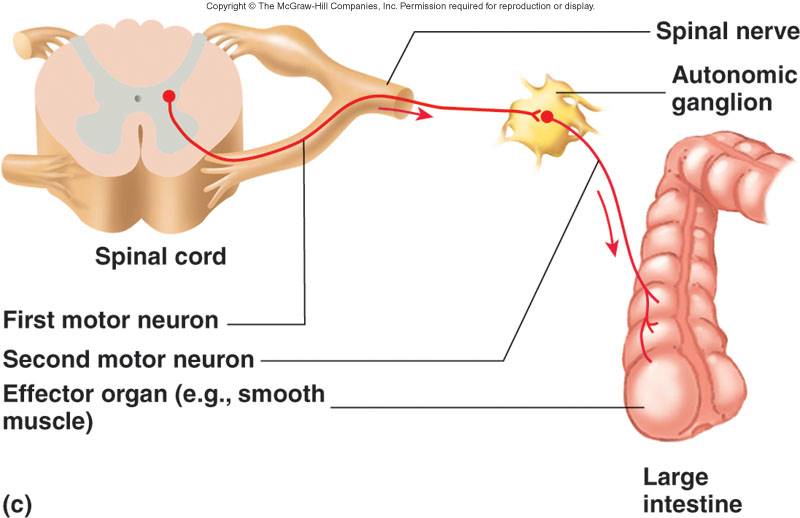
•from CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and certain glands.
•Somatic nervous system: from CNS to skeletal muscles.
–Voluntary.
–Single neuron system.
–Synapse: junction of a nerve cell with another cell. E.g., neuromuscular junction is a synapse between a neuron and skeletal muscle cell.
Autonomic nervous system (ANS):
•Organs receive dual innervations from both sympathetic and parasympathetic branches to maintain homeostasis
–Divisions of ANS
•Sympathetic. Prepares body for physical activity.
•Sympathetic (thoracolumbar)
–Fight or flight
•Parasympathetic. Regulates resting or vegetative functions such as digesting food or emptying of the urinary bladder.
•Enteric. plexuses within the wall of the digestive tract. Can control the digestive tract independently of the CNS, but still considered part of ANS because of the parasympathetic and sympathetic neurons that contribute to the plexi.
–Rest, relax, digest, eliminate
Neuronal Communication
•Cells produce electrical signals called action potentials
•Transfer of information from one part of body to another
•Electrical properties result from ionic concentration differences across plasma membrane and permeability of membrane
Age-Related Changes

•Decreased sensory receptors on skin
–Increased skin injury
•Slowing of action potential propagation
–Decreased neurons, decreased neurotransmitter receptors, decreased speed of transmission
•Decreased autonomic sensory function
–Bowel/bladder, BP regulation, H20 regulation
.