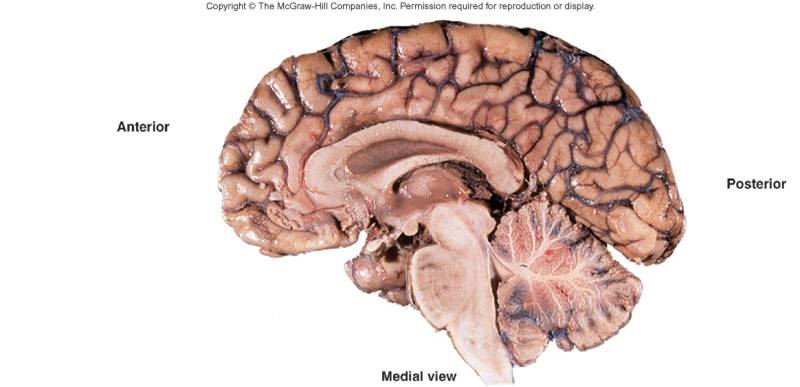
Brain
•Brain
•Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity
•Control center for many of body's functions
•Parts of the brain
•Cerebrum/cerebral cortex: conscious thought, control
•Brainstem: connects spinal cord to brain; integration of reflexes necessary for survival
•Cerebellum: involved in control of locomotion, balance, posture
•Diencephalon: thalamus, subthalamus, epithalamus, hypothalamus
Cerebrum
•Largest portion of brain
•Composed of right and left hemispheres each of which has the following lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, limbic, insular
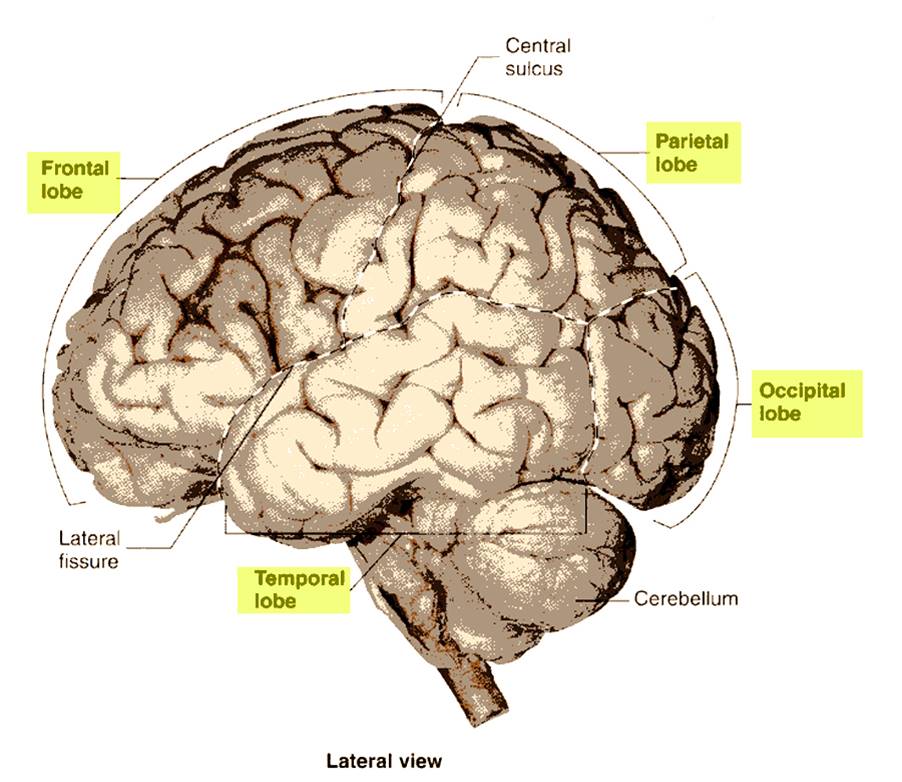
Cerebral Lobes
•Frontal: executor of function (voluntary motor function, motivation, aggression, sense of smell, mood)
•Parietal: sensory integrator for pain, temperature, detection of taste, and touch; coordinates reading
•Temporal: Reception and evaluation for smell and hearing; memory, abstract thought, judgment; Insula is within temporal lobe.
•Occipital: reception and integration of visual input
•Central sulcus: between the precentral gyrus (primary motor cortex) and postcentral gyrus (primary somatic sensory cortex)
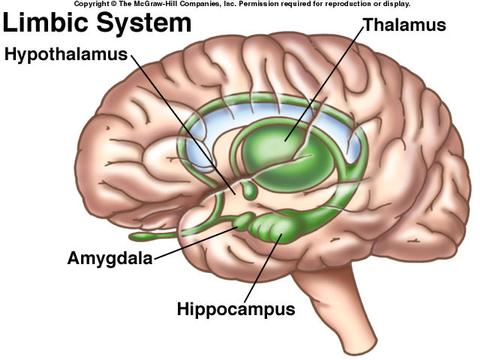
Limbic System
•Part of cerebrum and diencephalon
•Basic survival functions such as memory, reproduction, nutrition
•Emotions
•Various nuclei of the thalamus
•Part of the basal nuclei, hypothalamus, olfactory cortex, fornix