The Principles of Universal Design
Principle 5: Tolerance for Error
Definition
Tolerance for Error suggests minimizing hazards and the adverse consequences of accidental or unintended actions.
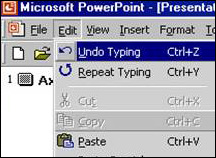 Example
Example
This is an example of a computer program that accommodates for user made errors. The program allows users to easily select an undo button to revert to an earlier copy of their work.
 Example
Example
The boardwalk trail through Muir Woods has been designed with edge protection along both sides of the trail. The edge protection serves as a safety measure by keeping people from walking or rolling off the trail unintentionally. It also serves as visitor management by discouraging people from disrupting the forests surrounding the giant redwoods.
Guidelines
- Arrange elements to minimize hazards and errors.
- Eliminate or minimize use of elements that are hazardous, isolated, or hidden.
- Provide warnings of hazards and errors.
- Provide fail-safe features.
- Discourage unconscious action in tasks that require vigilance.


