APTA PodCast on Osteoporosis
Clinical Significance of Bone Loss
- low BMD is a valid predictor of fracture risk
- common fractures: vertebral (compression), Colles's (distal radius with/without ulna) and hip
- fractures may precede trauma (spontaneous fracture causes the fall)
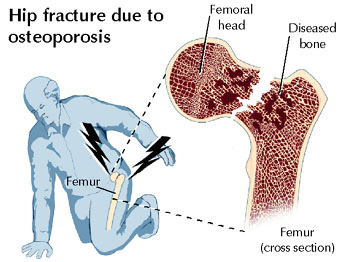
- disability and mortality rates associated with fracture are higher in population with lower bone densities
- increased rate of transition to skilled and assisted living settings post-fracture with osteoporosis
- prolonged immobilization due to illness or injury results in bone tissue loss
- activities requiring sustained or repeated trunk flexion may increase risk for compression fracture in the spine
Clinical Indicators of Bone Loss
- bone density studies (BMD)
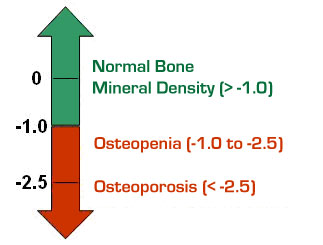
- outpatient procedure which measure bone density at the wrist, spine, hip, or calcaneus
- increased thoracic kyphosis
- loss of vertical height greater than one (1) inch
- stiffening of anterior trunk structure
- decreased shoulder flexion, ankle dorsiflexion, and hip extension
- decreased strength (hip extension, knee extension, abdominals, trunk extensors)
- trunk and/or visceral pain, radiating rib pain; point tenderness on spine
- fall risk on balance assessments
- Tinetti Assessment Tool
- Berg Balance Scale
- Supine Sign

- See Table 3-2 in Cameron and Monroe for a summary of clinical findings and prognoses
