Interventions
increase bone mass, slow bone loss, and/or reduce the risk of fractures.
Weight bearing aerobic exercise
depending on the severity of osteoporosis, patients may exercise in a weighted vest to stimulate osteoblastic activity
Resistance exercise
consistent effects are generally noted in spine bone density
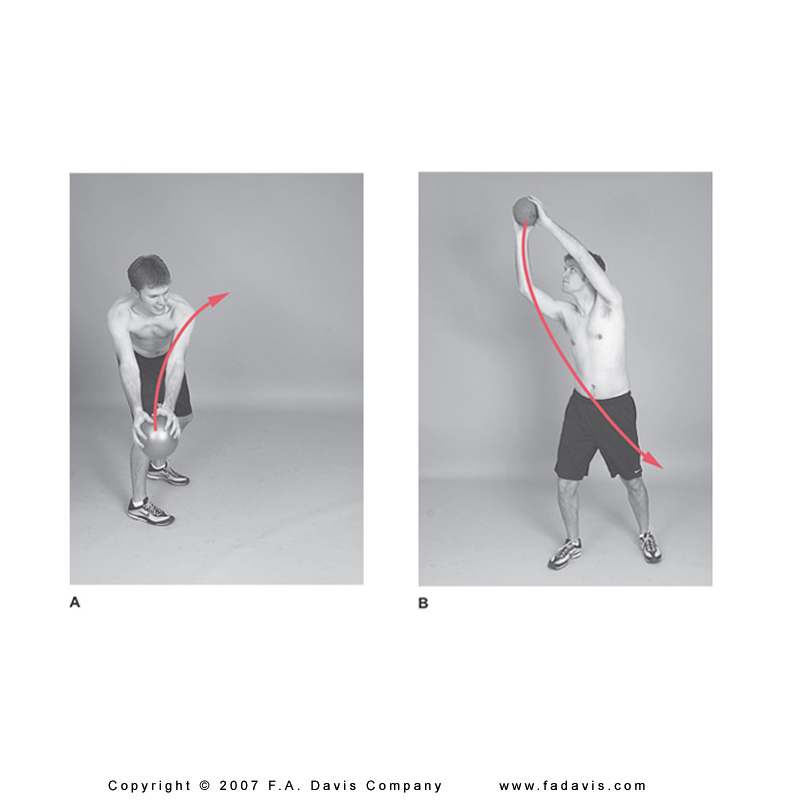
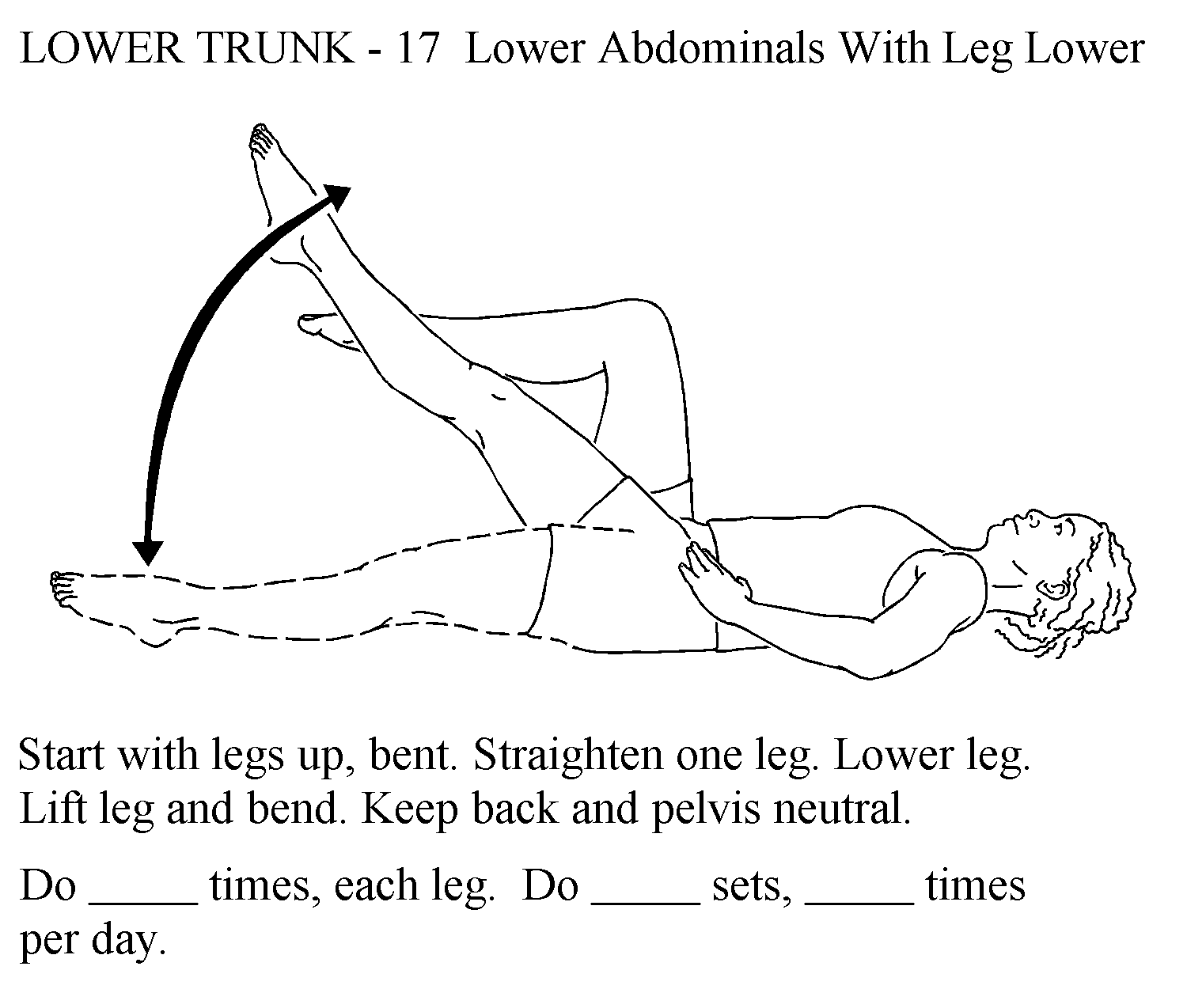
flexion activities (sit ups, abdominal machines) can increase pressure on compromised vertebral bodies and increase risk for fracture
no combined flexion with rotation exercises in trunk
limit closed chain hip internal/external rotation activities to decrease torsion through femoral neck
avoid high velocity, high impact activities
begin weight training at low intensities with low repetitions (6-8) to minimize fracture risk; progress to 1-3 sets of 8-12 repetitions of resisted exercise
an alternative to a curl up for abdominal strengthening is a straight leg raise with a stable lumbar and pelvic spine
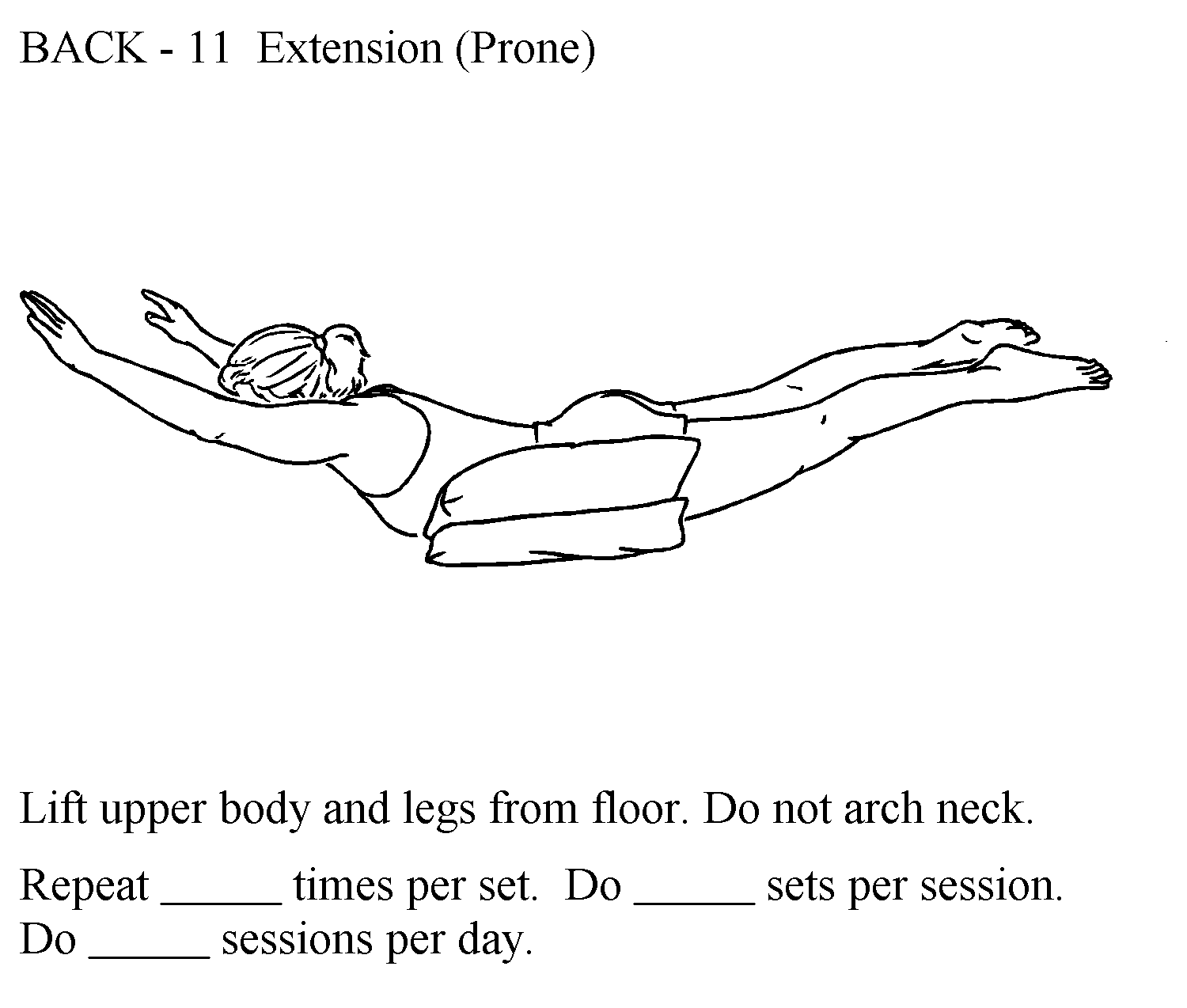
Spine exercises
strong evidence that back extension exercise can markedly reduce compression fracture risk
Body Mechanics Training
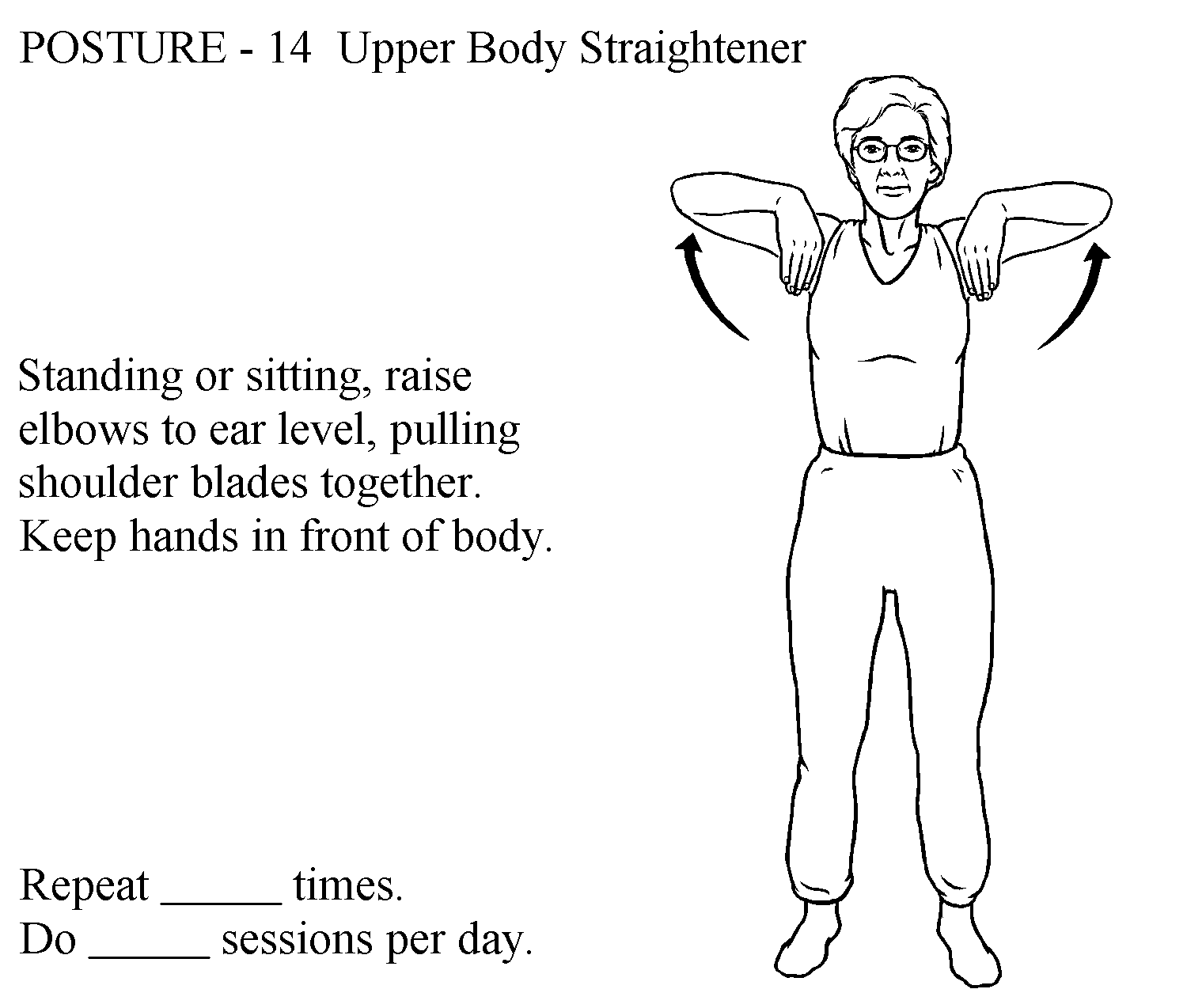
- posture awareness: emphasis on increasing control and activation of trunk extensors during postural activities, ADLs, and iADLs
- hip hinging
- hip and back extensor strengthening
- log rolling for bed mobility
- correct body mechanics for push/pull, lift, carry, etc.

Visit this recent New York Times Article about patient-centered interventions for fall prevention:
Orthoses
spinal orthoses can be customized or prefabricated for pain management and joint protection
![]()
 Dr. Weiß / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)
Dr. Weiß / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)
Fall prevention
exercises to target stiff and weak muscles should include some firm UE support to minimize risk for falls during unsupervised exercise
balance exercises: standing in a corner for safety or using a chair for support; narrow base of support and progressing to one leg
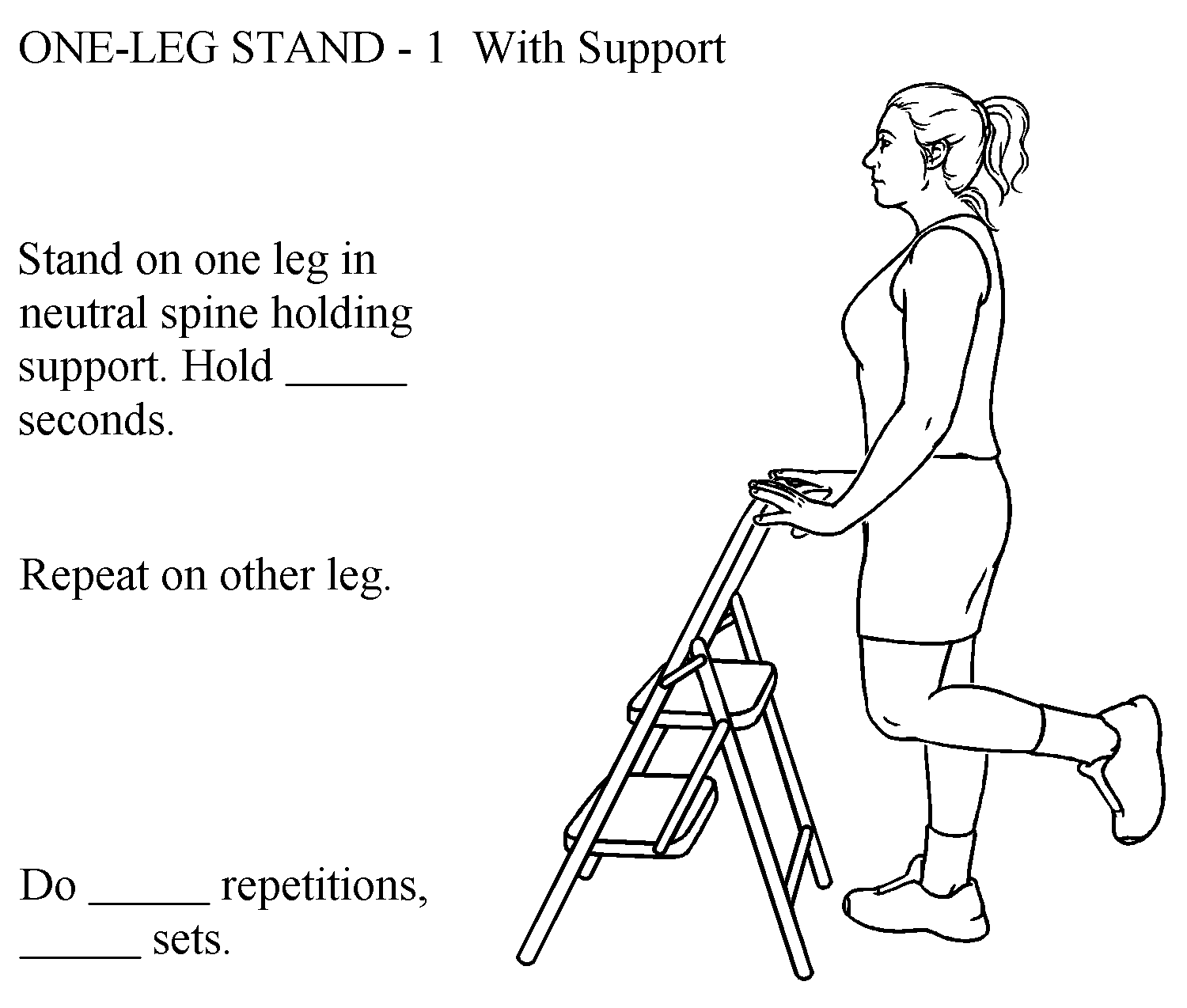
home assessment: identify areas and objects within the home that may increase risk for falls or repeated trunk flexion motions
Health and Wellness Education
- nutrition and lifestyle education: including dietary sources of calcium, magnesium and Vitamin D
- patients can self-assess fracture risk by using an online tool. Link to 'calculation tool' to select calculations normed by country of residence and race
Exercise Self-Test
Select the images which are most appropriate for strengthening in a patient with osteoporosis
|
A. |
B. |
C. |