Gastrointestinal (GI) Disorders
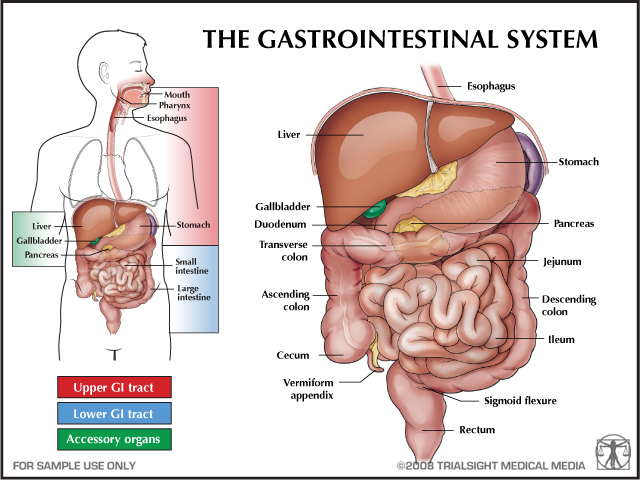
Common Causes
- Infections
- Autoimmune/immuno suppressives
- Genetic pre-disposition
- Lifestyle related: smoking, alcohol consumption (EtOH use), diet, stress
- Cancer
- Trauma
- Abdominal surgery: acute or history
Common Signs and Symptoms
- Nausea
- Vomiting (emesis)
- Anorexia
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Fluid and electrolyte imbalances
- Pain - abdominal and pain referred to abdominal region from another primary source
- Malnutrition
Common Treatments for GI Disorders
- Dietary modifications: reduction of nicotine, caffeine, alcohol
- Stress reduction
- Drugs
- Laxative
- Anti-diarrhea
- Antacids
- Analgesics
- Anti-emetic
- Surgical
- Gastric bypass
- Gland removal
- Bowel resection for bowel obstruction
- Hernia repair
Patient support equipment
Intravenous (IV) lines
- IV fluids administration
- Total Parental Nutrition (TPN - IV delivery of food and nutrients)
- Red blood cell infusions
Nutritional support
- Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tube
- Nasogastric (N-G) tube
- Red blood cell infusions
Fluid drains
Active drains use suction to remove fluids
• Jackson-Pratt drains (JP) – closed drain (has a collector) that aids in removing fluid from abdominal wounds.
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/10/Post-operative_Jackson-Pratt_Drains.JPG
• Sump drains – open drain that also removes fluid by suction
Passive drains use pressure differentials and/or gravity to remove fluid
• Foley catheter - indwelling tube that collects urine
• Colostomy bag - external bag that collects fecal waste
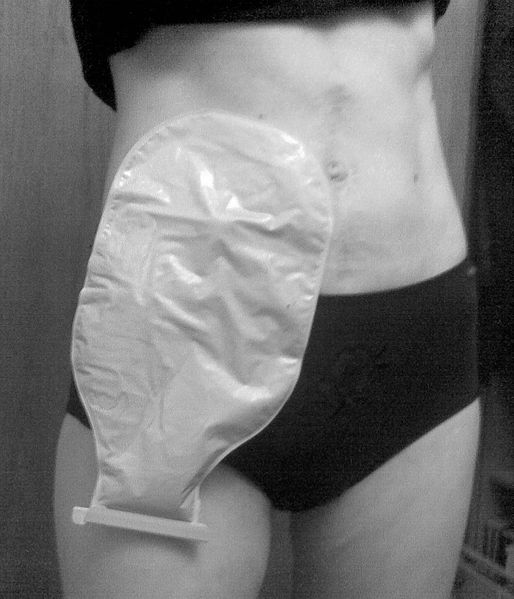
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ileostomy_with_bag.jpg

