Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Overview
- Increased risk with catheterization
- Increased risk with hospitalization
- Higher risk if a medical history of UTI's is present
- Higher incidence with individuals with diabetes and women.
- women have a shorter urinary tract which increases the risk (NYT, 2013)
- Most common cause is E Coli bacterial infection
- If untreated can lead to kidney infection and sepsis/septic shock
Signs and Symptoms
- Frequency of urination/urinary urgency
- Painful urination
- More common in men with UTI's than women with UTI's which is one of the reasons why UTI's are under diagnosed in women
- Burning feeling in the bladder
- Confusion
- Milky or cloudy urine
- Blood in urine
- Fever
- LBP
Urethritis and Cystitis
- Associated with sexually transmitted disease (STD)
- Signs and symptoms include increased frequency and urinary urgency
- Suprapubic pain, foul smelling urine, pyuria
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria, fatigue, anorexia, cognitive changes
- Results in pain, swelling of involved structure
- Treated with antibiotics and education/nursing care
Pyelonephritis

https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Douleur_fosse_lombaire_py%C3%A9lon%C3%A9phrite_-_Pyelonephritis.jpg
- Acute or chronic inflammation of renal pelvis, or parenchyma of kidney
- Infection ascends from lower urinary tract.
- Often pre-existing factor = hx of UTI's and or Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
- Signs and symptoms: mild sluggishness, s/sx cystitis, fever, chills, vomiting, malaise, severe flank pain, costovertebral tenderness on affected side
- Bacteriemia, septic shock
- Chronic pyelonephritis starts in medulla of kidney spreads to cortex.
Nephrolithiasis
- Problem primarily associated with the kidneys
- Kidney stones: crystallization of calcium, uric acid, magnesium-ammonium acetate
- Stones may form anywhere along the urinary tract
- Stone formation is associated with decreased fluid intake, low urine volume, genetic factors, bed rest and sedentary lifestyle
- Higher risk in areas of hot temperatures and high humidity
- S/sx similar to pyelonephritis marked increase in flank pain and urination pain

https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Blausen_0595_KidneyStones.png
Renal Trauma

- Blunt trauma: car, bicycle accidents, sports injuries, falls with injury to flank, abdomen or back
- Penetrating gun shot and/or stab wounds
- Renal trauma is diagnosed using ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, recent history, hematuria, intravenous pyelogram/IVP.
Psychosocial affects of Urinary Incontinence
- contributes to avoiding social activities, travel
- contributes to avoiding sexual encounters
Patient Support Equipment for Medical Management of Incontinence
-
Urethral catheters - tube placed in bladder via urethra
- Ureteral catheters - tube between kidney and urethra
- Suprapubic catheters -tube placed directly into superior aspect of bladder
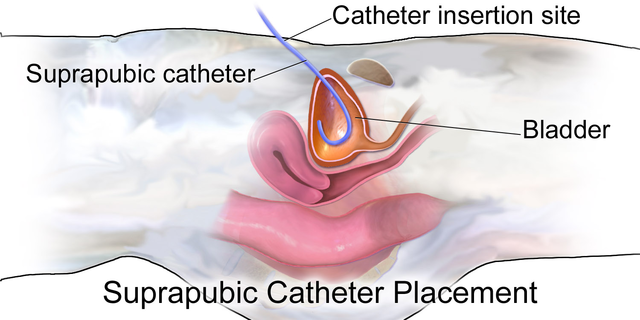
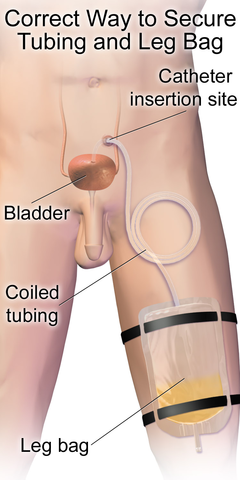
- Nephrostomy tubes
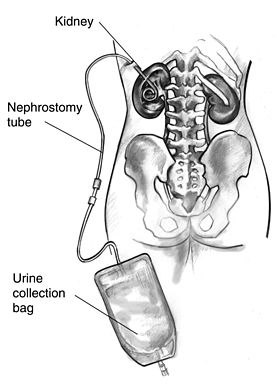
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nephrostomy
- Intermittent catheterization
Incontinence pads - these products are progressively improving to help support dignity and function

