Physical Therapy Role

PT Examination and Evaluation
The physical therapist prioritizes interventions within the physical therapy plan of care by integrating knowledge of body structure and function, participation restrictions, and contextual factors that inform prognosis and physical therapy diagnosis. Patient education in lifestyle factors that influence GI system disease should be integrated into a plan of care, with collaborative coordination with the medical and behavioral healthcare team as indicated. Patients with GI dysfunction may often present with comorbitites in the integument, cardiopulmonary, and musculoskeletal systems. Physical therapy providers should self-assess and seek opportunities for professional development specific to metabolic and GI dysfunction in order to minimize bias and reduce negative perceptions of patients in this population.
PT/PTA Relationship

• Maintain positive, open, timely, patient-centered communication
• Delegate and accept responsibilities for treatment based on the skill level of the PTA
• POC
– PT: Modify and update POC based on progress reported or reassessment
– PTA: Document patient status (progress/barriers) and request clarification or input as needed depending patient response and skill set
Role of the PTA
Tests and Measures
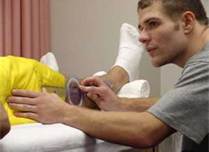
Aerobic Capacity and Endurance
- VS pre- post- activity, Borg RPE, O2 sats, observation for s/sx of cardiopulmonary response
Anthropometric Characteristics
- Height, weight, BMI, edema measures
Arousal, attention, cognition
- A&O, memory and recall
Pain
- VAS, faces scale, location, referral patterns
Joint Integrity and Mobility
- Range of motion(PROM/AROM) extremities and trunk
Neuromuscular tests
- Sensation and reflexes
- Strength
- Coordination
Functional Activity Performance
- FIM, Oswestry Disability Index
- Gait and locomotion
- Bending, lifting, carrying, reaching
Interventions for decreased endurance/aerobic capacity
1. Log rolling/bracing with pillow
2. Transfer training
3. Endurance training (gait, exercise)
4. Postural training
Interventions for impaired ventilation/respiration
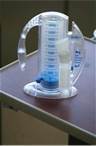
1. breathing exercises
2. incentive spirometry
3. huffing/directed cough
4. chest percussion and vibration
Interventions for Impaired integument integrity
1. Wound care for incisions
2. Skin/wound care for ostomies
3. Generalized skin care and education skin inspection for at-risk areas
Interventions for Decreased ADLs and Self-Care
1. Training in adaptive devices and equipment
2. Environmental assessment and modifications
Interventions for Disability Prevention and Wellness

Education in
1. Lifestyle modification/decreasing risk of recurrence
2. Energy conservation (pacing and prioritizing)
3. Ostomy care

