Genitourinary Diseases and Disorders
Urinary System
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Illu_urinary_system.jpg
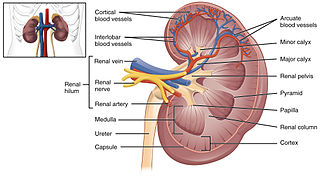
Anatomy
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/87/2610_The_Kidney.jpg/320px-2610_The_Kidney.jpg
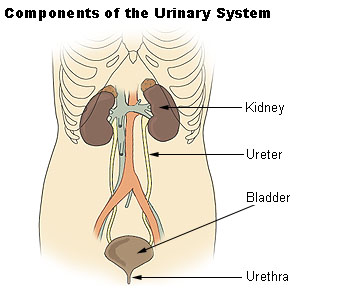
- Primary components
- Kidneys
- Ureter
- Bladder
- Urethra
- Secondary Components
- Prostate
- Pelvic Floor Muscles
- Genitals
Physiology
Fluids are filtered through the kidneys and the filtrate is converted to urine. Urine is mostly water and urea, which is a metabolic by-product of protein metabolism, and electrolytes
Urination is mediated by voluntary and involuntary nervous system actions:
- L1-L3 forms the sympathetic branch
- S2-S4 forms the parasympathetic branch - visceral and afferent pathways
Selected GU Medical Terminology
- Dysuria = abnormal urine/urination. Incontinence is a form of dysuria
- Incontinence = involuntary loss of urine. Incontinence can be
- urge - sensation of needing to urinate - overactive
- stress - muscular insufficiency
- overflow - insufficient bladder emptying or urethra blockage
- functional - unable to find/get to the toilet in time
- Enuresis= involuntary voiding during sleep
- Voiding =emptying urine from bladder
- Micturition = urination (Link to animation of the micturition reflex)
- Hematuria = blood in urine
- Pyuria = presence of pus/bacterial infection in urine
- Urgency = sensation of need to urinate, may be neurological or due to a spasm of smooth muscle in the bladder

